Home > Press > Nanoscale chemically ordered-disordered domains in Fe3Pt alloys and their three-dimensional interface and lattice strain
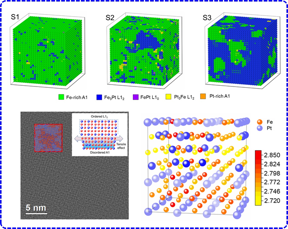 |
| The three-dimensional distribution of the Fe3Pt alloys prepared in this study with different degrees of chemical ordering is plotted in the figure (top). The size of ordered/disordered nanodomains and the lattice strain observed by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy is shown schematically in the lower left, and the magnetic moment modulation around the ordered/disordered interfaces is shown in the lower right. CREDIT ©Science China Press |
Abstract:
In solid-state matters, chemical ordering is often closely associated with their fantastic physical properties and specific chemical reaction mechanisms. Through the redistribution of atoms and chemical bonds, the modulation of chemical ordering can lead to effective lattice tuning and provide intrinsic lattice stress. However, the direct probing of the three-dimensional structure of chemically ordered/disordered interfaces remains a great challenge. Recently, the National Science Review published online the research results of Prof. Xianran Xing's group at the Institute of Solid State Chemistry, University of Science and Technology Beijing, which reveals the atomic distribution and lattice matching relationship of nano-scale ordered/disordered domains in Fe3Pt alloys with the help of the Pair Distribution Function (PDF) method. Through the lattice adjustment around the interfaces of nanodomains, the effective regulation of the magnetic properties and negative thermal expansion of lattice was obtained.
Nanoscale chemically ordered-disordered domains in Fe3Pt alloys and their three-dimensional interface and lattice strain
Beijing, China | Posted on May 27th, 2022The present experimental and theoretical results from the research team provide convincing structural insights into the identification of the local structure of nanodomains in solids and the lattice matching around the interfaces, providing a structural basis for understanding chemical ordering at the atomic scale and developing new lattice design strategies.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Bei Yan
Science China Press
Office: 86-10-64015905
Expert Contacts
Qiang Li
Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Materials Genome Engineering, Institute of Solid State Chemistry, University of Science and Technology Beijing
Xianran Xing
Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Materials Genome Engineering, Institute of Solid State Chemistry, University of Science and Technology Beijing
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








