Home > Press > Intense monocycle terahertz pulses from shifting electrons in quantum structures
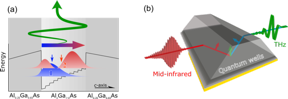 |
| Fig. 1. Ultrafast shift current generation in asymmetric semiconductor quantum wells and optical geometry. (a) Electrons are confined within a 13-nm wide quantum well made from AlxGa1-xAs. By varying the aluminum content one obtains an asymmetric (‘triangular’) potential, sandwiched between potential barriers. Quantum confinement leads to the formation of discrete energy levels 1 and 2 of electrons along the c axis. The contours are the spatially shifted probability distributions of electrons in the ground state (blue) and in the first excited state (red). The blue and red arrows mark the centers of gravity of the respective distribution. Electrons are promoted from state 1 to state 2 by an ultrashort mid-infrared pulse, resulting in a time-dependent spatial shift of electron position, which represents a time-dependent electric current. This so-called shift current emits a mono-cycle THz pulse. (b) Optical geometry of the THz source. 20 quantum wells are stacked at the bottom of a prism structure. They are excited by a femtosecond mid-infrared pulse (red transient, left). The THz pulses emitted in forward direction (green transient, right) are analyzed in the experiment. The height of the prism structure is approximately 350 µm. CREDIT MBI |
Abstract:
A time-dependent electric current emits an electromagnetic wave, a basic physical effect exploited in telecom antennas. Transferring this mechanism to the ultrashort length and time scales of the quantum world allows for generating intense picosecond terahertz (THz) pulses in asymmetric semiconductor quantum structures. The THz pulses display a single oscillation of the electric field and can be tailored via the nonlinear generation process.
Intense monocycle terahertz pulses from shifting electrons in quantum structures
Berlin, Germany | Posted on January 7th, 2022THz waves are an important analytical tool in science and technology, with applications ranging from materials and tissue characterization to security checks at airports. Ultrashort THz pulses with a duration of a few picoseconds (1 ps = 10-12 s) and high electric-field amplitudes are used in time-resolved spectroscopy of condensed matter. Moreover, they play a key role in telecommunication at ultrahigh data transmission rates. The strong potential of THz methods and technology calls for the development of efficient and compact THz sources.
Scientists from the Max-Born-Institute and the Paul-Drude-Institute in Berlin, Germany, have now demonstrated a novel concept for generating ultrashort THz waveforms by tailoring electronic currents in a compact optically driven quantum device [Optica 8, 1638 (2021)]. A mid-infrared driving pulse generates a time-dependent electric current in a highly compact semiconductor structure consisting of 20 asymmetric nanometer-thick quantum wells. This current emits THz pulses, which consist of a single THz oscillation cycle with a peak electric field amplitude of up to several kilovolts/cm. The time structure of the THz pulses can be tailored via the excitation conditions of the quantum device.
The basic mechanism of THz generation is illustrated in Figure 1. Electrons are spatially confined in a quasi-two-dimensional potential well, which is asymmetric along the stacking axis (c axis) of the AlxGa1-xAs semiconductor layers. Due to the narrow width of the potential well, electron quantum states 1 and 2 with different (minimum) energies arise, the so-called subbands. The asymmetric shape of the potential along the c axis results in spatially shifted probability distributions of electrons in the two subbands. Upon electron excitation from subband 1 to subband 2 by a mid-infrared pulse, the overall electron density experiences a time-dependent spatial shift of several nanometers within the asymmetric well. This transient spatial charge shift is equivalent to a time-dependent current. According to the basic laws of electrodynamics, this so-called shift current emits an electric field. For a femtosecond duration of the driving pulse, the frequency of the emitted field is in the THz range.
Figure 2 displays the emitted THz electric field as a function of time, as measured for different strengths of the mid-infrared driving pulse. All THz pulses are monocycles, i.e., the THz field oscillates only once during the pulse. The shape of the THz waveforms changes with the strength of the driving pulses, due to the nonlinear character of the generation process. This fact can be exploited to tailor the THz waveforms in a wide parameter range. The overall THz generation efficiency of up to several percent of the driving mid-infrared field makes this scheme particularly interesting for generating versatile THz pulses in highly compact optoelectronic sources working at, e.g., gigahertz repetition rates.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alexandra Wettstein
Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI)
Office: 0049-306-392 x1402
Expert Contacts
Prof. Dr. Thomas Elsaesser
Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy
Office: +49 30 6392 1400
Dr. Michael Woerner
Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy
Office: +49 30 6392 1470
Matthias Runge
Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy
Office: +49 30 6392 1471
Copyright © Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Quantum Computing
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








