Home > Press > Efficient photon upconversion at an organic semiconductor interface
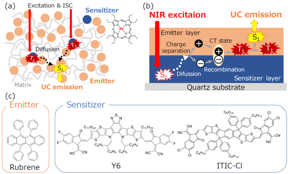 |
| Fig. 1 (a) Schematic illustrations of the conventional UC mechanism in films, and chemical structure of conventional sensitizer. (b) Schematic illustrations of the novel UC mechanism at the organic semiconductor interface. (c) Chemical structures of sensitizer and emitter of the novel UC systems. CREDIT NINS/IMS |
Abstract:
Photon upconversion (UC) is a process in which a material increases the energy of incident photons, resulting in the emission of photons with higher energies. The potential applications of UC include the recovery of wasted low-energy photons in photovoltaics and photocatalysis. In addition, near-infrared (NIR) to-visible UC, offering the advantage of high penetration in living tissues, is desired for biosensing, optogenetics, and photodynamic therapy. The conventional UC system relies on a triplet formation from an absorbed photon by intersystem crossing (ISC), which is typically facilitated by heavy-atom effect in a sensitizer molecule (Fig. 1a). The two triplet excitons form high energy one singlet by an annihilation process. Finally, the UC emission occurs from an emitter molecule. However, the conventional solid-state UC is still inefficient, exhibiting a highest external quantum efficiency (EQE) of less than 0.1%, which remains the greatest challenge inhibiting its real-life applications.
Efficient photon upconversion at an organic semiconductor interface
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on November 19th, 2021Group of Assistant Professor Seiichiro Izawa and Professor Masahiro Hiramoto at Institute for Molecular Science in Japan report that novel UC systems with heterojunctions of bilayer films of organic semiconductors (Fig. 1b). The mechanism of the first step involved in the novel UC relies on the charge separation at the sensitizer/emitter interface, thereby converting the photoexcited sensitizer singlet to free charges. This process is the same as the photoconversion at the electron donor/acceptor interface in organic photovoltaics. Subsequently, the free charges recombine to form the triplet at the interface. The UC emission is observable after the triplet-triplet annihilation. The sensitizer/emitter molecules used in the novel UC system (Fig. 1c) do not contain heavy atoms because the mechanism does not rely on ISC. According to the proposed mechanism, the entire pure sensitizer layer can absorb the incident light and contribute to the UC process. As a result, the solid-state UC system is achieved with the EQE of two orders of magnitude higher than those of the conventional systems, with an irradiation intensity about 100 mW/cm2, which is similar with standard solar fluence. The efficient UC enabled a demonstration of bright yellow emission on a flexible thin film by a NIR light-emitting diode excitation (Fig. 2). The novel UC system does not need strong laser excitation and the expensive platinum-group metals, rare-earth metals, or toxic elements. The finding leads to important applications of UC in flexible solar cells, bioimaging, and optogenetics.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hayao KIMURA
National Institutes of Natural Sciences
Office: 81-354-251-890
Expert Contact
Seiichiro Izawa
Institute for Molecular Science
Office: 81-564-59-5537
Copyright © National Institutes of Natural Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Organic Electronics
![]() New insights into energy loss open doors for one up-and-coming solar tech November 18th, 2022
New insights into energy loss open doors for one up-and-coming solar tech November 18th, 2022
![]() Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Scientists have proposed a new material for perovskite solar cells: It is cheaper its analogues, easier to manufacture and to modify October 28th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








