Home > Press > Taking 2D materials for a spin: Scientists at the University of Tsukuba and the Institute of High Pressure Physics fabricate a novel molybdenum disulfide transistor and create an image of the spins of the electrons passing through which may open the way for new spintronic compute
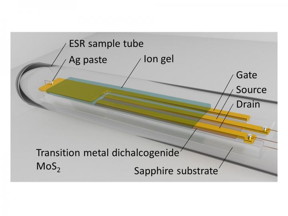 |
| Schematic diagram of the MoS2 transistor in an ESR sample tube. CREDIT University of Tsukuba |
Abstract:
Scientists from the University of Tsukuba and a scientist from the Institute of High Pressure Physics detected and mapped the electronic spins moving in a working transistor made of molybdenum disulfide. This research may lead to much faster computers that take advantage of the natural magnetism of electrons, as opposed to just their charge.
Taking 2D materials for a spin: Scientists at the University of Tsukuba and the Institute of High Pressure Physics fabricate a novel molybdenum disulfide transistor and create an image of the spins of the electrons passing through which may open the way for new spintronic compute
Tsukuba, Japan and Warsaw, Poland | Posted on March 5th, 2021Spintronics is a new area of condensed matter physics that attempts to use the intrinsic magnetic moment of electrons, called "spins," to perform calculations. This would be a major advance over all existing electronics that rely solely on the electron charge. However, it is difficult to detect these spins, and there are many unknowns regarding materials that can support the transport of spin-polarized electrons.
Now, an international research team led by the Division of Materials Science at the University of Tsukuba has successfully used electron spin resonance (ESR) to monitor the number and location of unpaired spins coursing through a molybdenum disulfide transistor. ESR uses the same physical principle as the MRI machines that create medical images. The spins are subject to a very strong magnetic field, which creates an energy difference between electrons with spins aligned and anti-aligned with the field. The absorbance of photons that match this energy gap can be measured to determine the presence of unpaired electron spins.
The experiment required the sample to be cooled to just four degrees above absolute zero, and the transistor to be in operation while the spins are being measured. "The ESR signals were measured simultaneously with the drain and gate currents," corresponding author Professor Kazuhiro Marumoto says. "Theoretical calculations further identified the origins of the spins," coauthor Professor Ma?gorzata Wierzbowska says. Molybdenum disulfide was used because its atoms naturally form a nearly flat two-dimensional structure. The molybdenum atoms form a plane with a layer of sulfide ions above and below.
The team found that charging the system with the additional electrons in a process called n-type doping was important for creating the spins. "In contrast with previous work on other 2D materials, the n-type doping allowed us to achieve better control of the electronic spins," Professors Marumoto and Wierzbowska explain. The scientists believe that molybdenum disulfide will prove to be an important testbed for spintronic devices as the technology advances towards future consumer products.
####
Contacts:
Naoko Yamashina
81-298-532-066
Copyright © University of Tsukuba
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
![]() Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








