Home > Press > New technique builds super-hard metals from nanoparticles
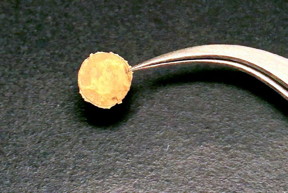 |
| This gold "coin" was made from nanoparticle building blocks, thanks to a new technique developed by Brown University researchers. Making bulk metals this way allows for precise of the metal's microstructure, which enhances its mechanical properties. CREDIT Chen Lab / Brown University |
Abstract:
Metallurgists have all kinds of ways to make a chunk of metal harder. They can bend it, twist it, run it between two rollers or pound it with a hammer. These methods work by breaking up the metal's grain structure -- the microscopic crystalline domains that form a bulk piece of metal. Smaller grains make for harder metals.
New technique builds super-hard metals from nanoparticles
Providence, RI | Posted on January 22nd, 2021Now, a group of Brown University researchers has found a way to customize metallic grain structures from the bottom up. In a paper published in the journal Chem, the researchers show a method for smashing individual metal nanoclusters together to form solid macro-scale hunks of solid metal. Mechanical testing of the metals manufactured using the technique showed that they were up to four times harder than naturally occurring metal structures.
"Hammering and other hardening methods are all top-down ways of altering grain structure, and it's very hard to control the grain size you end up with," said Ou Chen, an assistant professor of chemistry at Brown and corresponding author of the new research. "What we've done is create nanoparticle building blocks that fuse together when you squeeze them. This way we can have uniform grain sizes that can be precisely tuned for enhanced properties."
For this study, the researchers made centimeter-scale "coins" using nanoparticles of gold, silver, palladium and other metals. Items of this size could be useful for making high-performance coating materials, electrodes or thermoelectric generators (devices that convert heat fluxes into electricity). But the researchers think the process could easily be scaled up to make super-hard metal coatings or larger industrial components.
The key to the process, Chen says, is the chemical treatment given to the nanoparticle building blocks. Metal nanoparticles are typically covered with organic molecules called ligands, which generally prevent the formation of metal-metal bonds between particles. Chen and his team found a way to strip those ligands away chemically, allowing the clusters to fuse together with just a bit of pressure.
The metal coins made with the technique were substantially harder than standard metal, the research showed. The gold coins, for example, were two to four times harder than normal. Other properties like electrical conduction and light reflectance were virtually identical to standard metals, the researchers found.
The optical properties of the gold coins were fascinating, Chen says, as there was a dramatic color change when the nanoparticles were compressed into bulk metal.
"Because of what's known as the plasmonic effect, gold nanoparticles are actually purplish-black in color," Chen said. "But when we applied pressure, we see these purplish clusters suddenly turn to a bright gold color. That's one of the ways we knew we had actually formed bulk gold."
In theory, Chen says, the technique could be used to make any kind of metal. In fact, Chen and his team showed that they could make an exotic form of metal known as a metallic glass. Metallic glasses are amorphous, meaning they lack the regularly repeating crystalline structure of normal metals. That gives rise to remarkable properties. Metallic glasses are more easily molded than traditional metals, can be much stronger and more crack-resistant, and exhibit superconductivity at low temperatures.
"Making metallic glass from a single component is notoriously hard to do, so most metallic glasses are alloys," Chen said. "But we were able to start with amorphous palladium nanoparticles and use our technique to make a palladium metallic glass."
Chen says he's hopeful that the technique could one day be widely used for commercial products. The chemical treatment used on the nanoclusters is fairly simple, and the pressures used to squeeze them together are well within the range of standard industrial equipment. Chen has patented the technique and hopes to continue studying it.
"We think there's a lot of potential here, both for industry and for the scientific research community," Chen said.
###
Chen's coauthors on the paper were Yasutaka Nagaoka, Masayuki Suda, Insun Yoon, Na Chen, Hanjun Yang, Yuzi Liu, Brendan A. Anzures, Stephen W. Parman, Zhongwu Wang, Michael Grünwald and Hiroshi M. Yamamoto. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (CMMI-1934314, DMR-1332208, DMR-1848499) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DE-AC02-06CH11357).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Stacey
401-863-3766
@brownuniversity
Copyright © Brown University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Industrial
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
![]() Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
Nanotubes: a promising solution for advanced rubber cables with 60% less conductive filler June 1st, 2022
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
OCSiAl receives the green light for Luxembourg graphene nanotube facility project to power the next generation of electric vehicles in Europe March 4th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








