Home > Press > Chemists get peek at novel fluorescence: Rice University scientists discover delayed phenomenon in carbon nanotubes
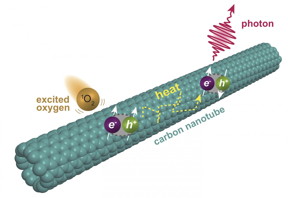 |
| Chemists at Rice University have discovered a second level of fluorescence in single-walled carbon nanotubes. The fluorescence is triggered when oxygen molecules excited into a singlet state interact with nanotubes, prompting excitons to form triplet states that upconvert into fluorescing singlets. (Credit: Illustration by Ching-Wei Lin/Rice University) |
Abstract:
That carbon nanotubes fluoresce is no longer a surprise. Finding a second level of fluorescence is surprising and potentially useful.
Chemists get peek at novel fluorescence: Rice University scientists discover delayed phenomenon in carbon nanotubes
Houston, TX | Posted on December 3rd, 2020How does it work? Wait for it.
The Rice University lab of Bruce Weisman, a professor of chemistry who led the pioneering discovery of nanotube fluorescence in 2002, found that single-walled nanotubes emit a delayed secondary fluorescence when triggered by a multistep process in a solution with dye molecules and dissolved oxygen.
The delay is only microseconds, but it’s enough to be detected with some effort.
The complex process is detailed by Weisman, lead author and Rice alumnus Ching-Wei Lin and research scientist Sergei Bachilo in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
The reaction begins when light excites a solution containing a dye called rose bengal. Oxygen molecules dissolved in the solution capture energy from the dye, forming energized O2. These then transfer their energy to nanotubes, where excitons -- quasiparticles made of electrons and electron holes -- are generated in their triplet state. With a bit of added thermal energy, those excitons get promoted to a higher energy singlet state that emits the observed fluorescence.
“For a number of years, we have been looking at interesting effects involving nanotubes and oxygen,” Weisman said. “We’ve found quite a range of things that can happen, from physical effects like this energy transfer or the reversible quenching of fluorescence, to the triggering of chemical reactions between nanotubes and DNA. So this study was part of a larger program of exploration.”
Their ability to excite dissolved oxygen molecules prompted the researchers to see how that would affect adjacent nanotubes, Weisman said.
“We make singlet oxygen by exciting a dye molecule with visible light, and then the oxygen deactivates the dye and gets excited itself,” he said. “That idea goes back decades in photophysics and is very conventional. What’s unusual here is that the singlet oxygen interacts with the nanotube to directly make triplet-state excitations in the tube. Those triplet states have been pretty elusive.
“Triplet states of organic molecules are the longest-lived excited states,” Weisman said. “Their lifetimes are orders of magnitude greater than the singlet excited states, so they can hang around long enough to bump into something else and undergo chemical reactions.
“But because nanotube triplet states don’t emit light or directly absorb light very well, they are tricky to study and not too much is known about them,” he said. “What we’ve been doing is trying to understand them a little better.”
Triggering fluorescence still required an extra step. “Just by random thermal agitation in their surroundings, these guys can sometimes get kicked up to the bright singlet state, and then they can tell you they’re there by spitting out a photon,” Weisman said.
Because the triplet state can last 10 microseconds or so, that upconverted emission is called delayed fluorescence.
The researchers had to find a way to detect the relatively weak effect amid the nanotubes’ bright primary fluorescence. “It was like trying to see a dim object right after being blinded by a bright camera flash,” Weisman said. “We had to devise some special instrumentation.”
One device “is basically a fast mechanical shutter” that covers the short-wave infrared (SWIR) spectrometer during the bright flash and then quickly opens up, a kind of reverse camera that goes from covered to open in seven microseconds. The other device, he said, is a sensitive detector that’s triggered with an electronic signal and measures how the weak emission fades away over time. “These systems were both built by Ching-Wei, who’s a terrific experimentalist,” he said.
Weisman and colleagues have employed nanotube fluorescence in medical imaging technologies and in nanotube-based smart skin to measure strain in surfaces, among other applications. He said the new discovery could eventually find its way into optoelectronics and solar energy.
“There’s not a direct step where somebody’s going to read this and make a new, more efficient device,” Weisman said. “But this fundamental knowledge of processes and properties is the foundation on which new technologies are built.”
The National Science Foundation and the Welch Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,978 undergraduates and 3,192 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Nanotubes are beacons in cancer-imaging technique:
Nanotubes are beacons in cancer-imaging technique:
![]() Researchers advance techniques to detect ovarian cancer:
Researchers advance techniques to detect ovarian cancer:
![]() ‘Smart skin’ simplifies spotting strain in structures:
‘Smart skin’ simplifies spotting strain in structures:
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








