Home > Press > Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes
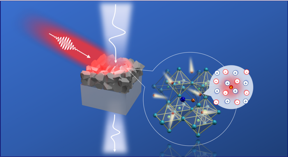 |
| The photoexcited charge carrier is “dressed” by the local lattice distortion, which is revealed by ultrafast conductivity measurements using terahertz transient. CREDIT by Zuanming Jin, Yan Peng, Yuqing Fang, Zhijiang Ye, Zhiyuan Fan, Zhilin Liu, Xichang Bao, Heng Gao, Wei Ren, Jing Wu, Guohong Ma, Qianli Chen, Chao Zhang, Alexey V. Balakin, Alexander P. Shkurinov, Yiming Zhu, Songlin Zhuang |
Abstract:
Organic-inorganic hybrid metal halide perovskites (MHPs) have attracted tremendous attention for optoelectronic applications. For example, cost-effective solar cells, solid-state lighting, memristors, and ultrafast spin switches in spintronics have recently been designed using MHPs. Despite the promise of the material, many questions remain regarding the nature and mobility of charge carriers in MHPs, which require further understanding.
Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes
Changchun, China | Posted on July 8th, 2022Researchers from the University of shanghai for science and technology, in collaboration with Qingdao institute of bioenergy and bioprocess technology, Shanghai University, Shanghai institute of technical physics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Lomonosov Moscow State University, now report photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes.
The researchers experimentally identify the photocarriers-optical phonon coupling in CH3NH3PbI3 (MAPbI3) polycrystalline grains, by using optical-pump and terahertz-electromagnetic probe spectroscopy. The photoinduced charge carrier, together with the surrounding lattice distortion over several lattice constants, forms a quasi-particle - a polaron. Using the Drude-Smith-Lorentz model along with the Frӧhlich-type electron-phonon coupling, the researchers determine the effective mass and scattering parameters of photogenerated polaronic carriers. According to the polaron mass enhancement, the polycrystalline nature of the material, and the presence of defects, the large polaron mobility is calculated on the order of ~80 cm2V−1s−1.
Furthermore, the researchers reveal that the formation of large polarons in MAPbI3 protects the charge carriers from scattering with polycrystalline grain boundaries or defects and explains the long lifetime of photoconductivity. The findings provide insights into the polaronic nature of charge carriers in MAPbI3 materials, which is relevant for both fundamental researches and device applications. The results are published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Yaobiao Li
Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
Office: 86-431-861-76851
Expert Contact
Yan Peng
University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Copyright © Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Perovskites
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Memristors
![]() Artificial neurons go quantum with photonic circuits: Quantum memristor as missing link between artificial intelligence and quantum computing March 25th, 2022
Artificial neurons go quantum with photonic circuits: Quantum memristor as missing link between artificial intelligence and quantum computing March 25th, 2022
![]() New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
![]() New insights into memristive devices by combining incipient ferroelectrics and graphene November 27th, 2020
New insights into memristive devices by combining incipient ferroelectrics and graphene November 27th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
![]() Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








