Home > Press > Russian scientists identified energy storage mechanism of sodium-ion battery anode
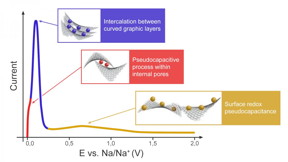 |
| A proposed model during desodiation of hard carbon CREDIT Zoia V.Bobyleva et al./Electrochimica Acta |
Abstract:
Scientists from Skoltech and Moscow State University (MSU) identified the type of electrochemical reaction associated with charge storage in the anode material for sodium-ion batteries (SIB), a new promising class of electrochemical power sources. Their findings along with the anode manufacturing method developed by the same team will help bring closer the SIB commercialization in Russia and beyond. The research was published in the journal Electrochimica Acta.
Russian scientists identified energy storage mechanism of sodium-ion battery anode
Moscow, Russia | Posted on July 24th, 2020Today lithium-ion batteries (LIB) are the most popular electrochemical power sources used in diverse applications running the gamut from mobile phones (several watt-hours) to buffer systems at power plants (millions of watt-hours). The demand for LIB and the average size of storage devices are constantly growing, however this growth trend is encountering multiple barriers, such the high cost of lithium salts, limited global reserves of lithium and uneven distribution of lithium-containing deposits across countries. To overcome these hurdles, scientists worldwide, Russia included, are working on SIB, an alternative technology that may challenge both LIB and the widely used lead-acid batteries.
Sodium is the sixth most common element in the Earth's crust. Its salts are about 100 times cheaper as compared to lithium. Although similar to lithium in terms of chemical properties, sodium has other distinctions that call for new approaches in SIB design. A battery is made up of three main components: the cathode, the anode and the electrolyte. There is a broad diversity of compositions and structures that could be suitable for SIB cathodes or electrolytes, whereas the anode still remains a stumbling block. Graphite, which is successfully used in LIB, does not work for SIB because the sizes of carbon hexagons and sodium cations differ too much to provide intercalation. Hard carbon seems to be the only material that can actually be used in the anode. Hard carbon formed by an irregular arrangement of distorted graphite-like layers demonstrates sodium-ion storage properties comparable to those of graphite in LIB, however it still remains unclear why and how this happens.
"There are several hypotheses as to how sodium could be introduced into hard carbon. In our study, we validated and slightly expanded one of them. We found that hard carbon exhibits intercalation-type behavior to accumulate most of the charge, which is great news. Intercalation is exactly what the battery needs, while the surface processes associated with "pseudocapacitance" are the responsibility of supercapacitors that form a very narrow niche among chemical power sources. Funnily enough, our Japanese colleague and research supervisor for our principal investigator and MSU PhD student, Zoya Bobyleva, held a totally different view at the start. He is one of the world's top experts in SIB and hard carbon and we had a hard time convincing him that we were right, but we did it!" says Oleg Drozhzhin, project lead and senior research scientist at Skoltech's Center for Energy Science and Technology (CEST) and MSU.
Last year, Nobel Prizes in Chemistry were awarded to three scientists "for the development of lithium-ion batteries". One of the winners owes his prize to hard carbon, an anode material that gave life to the LIB technology about three decades ago and was later replaced with graphite. Now hard carbon can once again give rise to a new technology.
"This work is remarkable not only in showing how hard carbon works in the sodium-ion system but also in finding a way to produce hard carbon with a capacity of over 300 mAh/g comparable to that of graphite in LIB. Creating and optimizing a new method takes a lot of painstaking effort that typically remains behind the scenes and is hardly ever reported in scientific papers, so it is important for us to show the ultimate result: we succeeded in making good anode materials for SIB and we know how they work," comments Evgeny Antipov, a Skoltech professor and head of the Department of Electrochemistry at the MSU Faculty of Chemistry.
###
The study was performed in collaboration with the Tokyo University of Science and the University of Strasbourg with financial support from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ilyana Zolotareva
897-777-14699
Copyright © Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








