Home > Press > Researchers review advances in 3D printing of high-entropy alloys: SUTD collaborates with universities in Singapore and China to shine light on HEA manufacturing processes and inspire further research in this emerging field
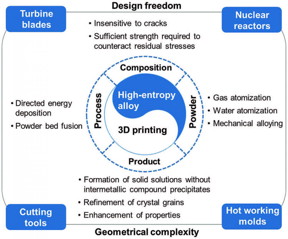 |
| Overview of the relationship between HEAs and 3D printing, with regard to the composition design, powder development, printing processes, product characteristics, and potential applications. CREDIT SUTD |
Abstract:
High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are at the frontier of the metal materials community. They are used as alternative materials in the production of high-temperature turbine blades, high-temperature molds and dies, hard coatings on cutting tools or even components of 4th generation nuclear reactors.
Researchers review advances in 3D printing of high-entropy alloys: SUTD collaborates with universities in Singapore and China to shine light on HEA manufacturing processes and inspire further research in this emerging field
Singapore | Posted on May 22nd, 2020By screening proper combinations of HEAs' constituent elements and regulating their proportions, HEAs can exhibit remarkable mechanical properties at high temperatures and display exceptional strength, ductility and fracture toughness at cryogenic temperatures.
Meanwhile, the development of HEAs for 3D printing has also been advancing rapidly, ramping up great potential for the manufacturing of such geometrically complex HEA products with desirable performances.
However, there is a lack of comprehensive understanding on the 3D printing of HEAs. To tackle this issue, researchers from Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Huazhong University of Science and Technology and Hunan University collaborated to publish a thorough review of the recent achievements on 3D printing of HEAs (refer to image). The study was published in Advanced Materials.
The review paper includes the production processes for HEA powders, 3D printing processes for HEA products, and the microstructure, mechanical properties, functionalities and potential applications of the printed products.
"3D printing of HEAs has been undergoing explosive growth in the academia and will gain extensive interest from industry. In our review, laser-based directed energy deposition, selective laser melting and electron beam melting are validated for their applicability to print various high-quality HEA products. It allows for a combination of material selection, design and manufacturing freedoms for lightweight, customizable and non-assembly required products," explained lead author Professor Chua Chee Kai from SUTD.
"The ultrafast cooling rates of certain 3D printing techniques are expected to prevent the formation of undesirable intermetallic compounds in HEA products, thereby enhancing their mechanical properties. The different cooling rates of these printing processes would induce substantial variations in both the microstructures and macroscopic performances of the products," said first author Dr Han Changjun from NTU.
"We believe that this paper serves as a valuable comprehensive review to deepen our understanding of the 3D printing of HEAs by focusing on its unique merits. Hopefully, more researchers would be encouraged to explore this highly interesting field," added corresponding author Associate Professor Zhou Kun from NTU.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jessica Sasayiah
656-499-4823
Copyright © Singapore University of Technology and Design
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
3D & 4D printing/Additive-manufacturing
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
Fiber sensing scientists invent 3D printed fiber microprobe for measuring in vivo biomechanical properties of tissue and even single cell February 10th, 2023
![]() 3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
3D-printed decoder, AI-enabled image compression could enable higher-res displays December 9th, 2022
![]() Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Researchers design new inks for 3D-printable wearable bioelectronics: Potential uses include printing electronic tattoos for medical tracking applications August 19th, 2022
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








