Home > Press > Molecules with a spin on a topological insulator: a hybrid approach to magnetic topological states of matter
 |
Abstract:
Controlling the interactions at the interface of a magnetic/topological insulator heterostructure is an outstanding challenge with implications in fundamental science and technology. A research led by the ICN2 Atomic Manipulation and Spectroscopy Group and the Physics and Engineering of Nanodevices Group, in collaboration with the Supramolecular Nanochemistry and Materials Group, the CFM-San Sebastián, ETH Zurich, ISM-Trieste and ALBA Synchrotron, has shown that ligands from metal-organic molecules can be used to tailor the properties of these interfaces. The results are presented in ACS Nano.
Molecules with a spin on a topological insulator: a hybrid approach to magnetic topological states of matter
Barcelona, Spain | Posted on May 1st, 2020A topological insulator (TI) is a material that behaves as an insulator in its interior but whose surface contains exotic conducting states, therefore allowing electrons to move only in the surface of the material. The most peculiar property of these surface electrons is that their spin is locked to the direction of motion, so that it can be manipulated by electrical currents.
Interfacing TIs with a magnetic material can give rise to phenomena such as the current-induced spin to charge interconversion and the emergence of dissipationless spin currents, which can be exploited in novel spintronic devices, metrology or in electron-spin based quantum information applications. However, this union of TI and magnetic material into a so-called heterostructure is a complex process that often prevents the control of the special phenomena described before. In particular, when the TI is interfaced directly with metallic ferromagnets, the strong interaction between the two materials leads to undesired effects such as the loss of magnetic properties or the suppression of the topological surface states.
By contrast, metal-organic molecules, organic molecules hosting a (magnetic) metallic ion, have been envisioned as candidates to develop magnetic/TI heterostructures in which interfacial interactions are tailored by the organic ligand. This is precisely what researchers from the ICN2, in collaboration with CFM-San Sebastián, ETH Zurich, ISM-Trieste and ALBA Synchrotron, have demonstrated. Published in ACS Nano, this research has been led by ICREA Prof. Aitor Mugarza, Leader of the Atomic Manipulation and Spectrocopy Group and ICREA Prof. Sergio O. Valenzuela, Leader of the Physics and Engineering of Nanodevices Group. They have had the collaboration of ICREA Prof. Daniel Maspoch, Leader of the Supramolecular Nanochemistry and Materials Group, which has synthesised the metal-organic molecule. The first author of the work is former ICN2’s PhD student Marc G. Cuxart.
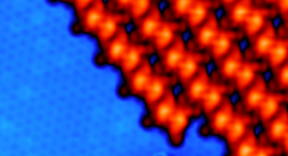
In this work, the researchers have shown for the first time that it is possible to tune the interfacial interaction without quenching the molecular spin and the topological surface state of the TI by choosing suitable organic ligands. In particular, they found that CoTBrPP and CoPc monolayers (metal-organic molecules) adsorbed on Bi2Te3 (topological insulator) form robust interfaces where electronic interactions can be tuned without strongly perturbing the intrinsic properties of each constituent. Their conclusions are supported by structural, electronic and magnetic information derived from a combination of specialised techniques (STM, ARPES, XMCD and DFT).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Francisco J. Pańos
Copyright © ICN2
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
![]() Study on Magnetic Force Microscopy wins 2023 Advances in Magnetism Award: Analysis of finite size effects reveals significant consequences for density measurements November 3rd, 2023
Study on Magnetic Force Microscopy wins 2023 Advances in Magnetism Award: Analysis of finite size effects reveals significant consequences for density measurements November 3rd, 2023
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
![]() Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling November 4th, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








