Home > Press > A twist connecting magnetism and electronic-band topology: Combined optical and torque measurements establish the microscopic mechanism linking magnetism and electronic-band topology in a Dirac material
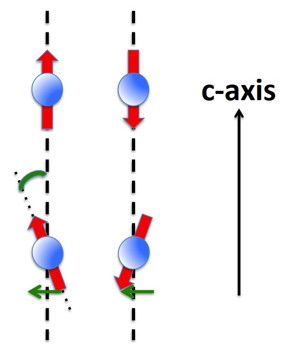 |
| Antiferromagnetic (top) and canted-antiferromagnetic order (bottom). In the latter case the spins are canted relative to the easy c-axis, leading to a ferromagnetic contribution in the plane orthogonal to that axis (represented by green arrows). CREDIT ETH Zurich/D-PHYS |
Abstract:
Dirac matter is an intriguing class of materials with rather peculiar properties: electrons in these materials behave as if they had no mass. The most prominent Dirac material is graphene, but further members have been discovered during the past 15 years or so. Each one of them serves as a rich playground for exploring 'exotic' electronic behaviours, some of which hold the promise to enable novel components for electronics. However, even if Dirac matter and other so-called topological materials --- in which electrons behave in similarly unexpected ways --- are among the currently most intensively studied condensed-matter systems, there are only very few examples where the topology of the electronic bands is connected in a well-defined manner to the magnetic properties of the materials. One material in which such interplay between topological electronic states and magnetism has been observed is CaMnBi2, but the mechanism connecting the two remained unclear. Writing in Physical Review Letters [1], postdoc Run Yang and PhD student Matteo Corasaniti from the Optical Spectroscopy group of Prof. Leonardo Degiorgi at the Laboratory for Solid State Physics of ETH Zurich, working with colleagues at Brookhaven National Laboratory (US) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, now report a comprehensive study in which they provide clear evidence that it is a slight nudge on the magnetic moments, known as spin canting, that provokes substantial changes in the electronic band structure.
A twist connecting magnetism and electronic-band topology: Combined optical and torque measurements establish the microscopic mechanism linking magnetism and electronic-band topology in a Dirac material
Zurich, Switzerland | Posted on April 7th, 2020Compass points to the right direction on a bumpy road
CaMnBi2 and the related compound SrMnBi2 have recently attracted attention as they display quantum magnetism -- the manganese ions are antiferromagnetically ordered at around room temperature and below -- and at the same time they host Dirac electrons. That there is interplay between the two properties has been suspected for some while, not least as at ~50 K there appears an unexpected 'bump' in the conduction properties at these materials. But the precise nature of this anomaly was still poorly understood until now.
In earlier work studying optical properties [2], Corasaniti, Yang and co-workers had established already a link to the electronic properties of the material. They used in particular the fact that the bump-like anomaly in the transport properties can be shifted in temperature by replacing some of the calcium atoms with sodium. To get now to the microscopic origins of the observed behaviour, they studied samples with different sodium dopings by torque magnetometry. In this technique, the torque on a magnetic sample is measured when it is exposed to a suitably strong field, similarly as a compass needle aligns with the Earth magnetic field. And this approach proved to point the team to the origins of the anomaly.
A firm link between magnetic and electronic properties
In their magnetic-torque experiments, the researchers found that at temperatures where no anomaly is observed in the electronic transport measurements, the magnetic behaviour is such as one would expect for an antiferromagnet. This was not the case anymore at temperatures at which the anomaly is present. There, a ferromagnetic component appeared, which can be explained by a projection of magnetic moments onto the plane orthogonal to the easy spin c-axis of the original antiferromagnetic order (see the figure). This phenomenon is known as spin-canting, induced by a so-called super-exchange mechanism.
These two sets of experiments -- optical and torque measurements -- were supported by dedicated first-principles calculations. In particular, for the case where spin canting was included in the calculations, a peculiar hybridization between the manganese and bismuth atoms was found to mediate the interlayer magnetic coupling and to govern the electronic properties in the material. Taken together, the study therefore establishes that sought-after direct link between the magnetic properties and changes to the electronic band structure, reflected in the bump anomaly of the transport properties.
With such detailed understanding on board, the door is now open to exploring not only the electronic properties of CaMnBi2 and related compounds, but also the possibilities arising from the connection between magnetic properties and topological states in these intriguing forms of matter.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andreas Trabesinger
@ETH_physics
Copyright © ETH Zurich Department of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








