Home > Press > Manipulating atoms one at a time with an electron beam: New method could be useful for building quantum sensors and computers
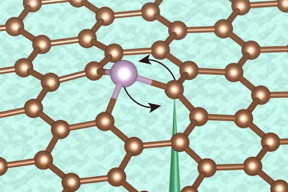 |
| This diagram illustrates the controlled switching of positions of a phosphorus atom within a layer of graphite by using an electron beam, as was demonstrated by the research team. Courtesy of the researchers |
Abstract:
The ultimate degree of control for engineering would be the ability to create and manipulate materials at the most basic level, fabricating devices atom by atom with precise control.
Manipulating atoms one at a time with an electron beam: New method could be useful for building quantum sensors and computers
Cambridge, MA | Posted on May 17th, 2019Now, scientists at MIT, the University of Vienna, and several other institutions have taken a step in that direction, developing a method that can reposition atoms with a highly focused electron beam and control their exact location and bonding orientation. The finding could ultimately lead to new ways of making quantum computing devices or sensors, and usher in a new age of "atomic engineering," they say.
The advance is described today in the journal Science Advances, in a paper by MIT professor of nuclear science and engineering Ju Li, graduate student Cong Su, Professor Toma Susi of the University of Vienna, and 13 others at MIT, the University of Vienna, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and in China, Ecuador, and Denmark.
"We're using a lot of the tools of nanotechnology," explains Li, who holds a joint appointment in materials science and engineering. But in the new research, those tools are being used to control processes that are yet an order of magnitude smaller. "The goal is to control one to a few hundred atoms, to control their positions, control their charge state, and control their electronic and nuclear spin states," he says.
While others have previously manipulated the positions of individual atoms, even creating a neat circle of atoms on a surface, that process involved picking up individual atoms on the needle-like tip of a scanning tunneling microscope and then dropping them in position, a relatively slow mechanical process. The new process manipulates atoms using a relativistic electron beam in a scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM), so it can be fully electronically controlled by magnetic lenses and requires no mechanical moving parts. That makes the process potentially much faster, and thus could lead to practical applications.
Using electronic controls and artificial intelligence, "we think we can eventually manipulate atoms at microsecond timescales," Li says. "That's many orders of magnitude faster than we can manipulate them now with mechanical probes. Also, it should be possible to have many electron beams working simultaneously on the same piece of material."
"This is an exciting new paradigm for atom manipulation," Susi says.
Computer chips are typically made by "doping" a silicon crystal with other atoms needed to confer specific electrical properties, thus creating "defects' in the material -- regions that do not preserve the perfectly orderly crystalline structure of the silicon. But that process is scattershot, Li explains, so there's no way of controlling with atomic precision where those dopant atoms go. The new system allows for exact positioning, he says.
The same electron beam can be used for knocking an atom both out of one position and into another, and then "reading" the new position to verify that the atom ended up where it was meant to, Li says. While the positioning is essentially determined by probabilities and is not 100 percent accurate, the ability to determine the actual position makes it possible to select out only those that ended up in the right configuration.
Atomic soccer
The power of the very narrowly focused electron beam, about as wide as an atom, knocks an atom out of its position, and by selecting the exact angle of the beam, the researchers can determine where it is most likely to end up. "We want to use the beam to knock out atoms and essentially to play atomic soccer," dribbling the atoms across the graphene field to their intended "goal" position, he says.
"Like soccer, it's not deterministic, but you can control the probabilities," he says. "Like soccer, you're always trying to move toward the goal."
In the team's experiments, they primarily used phosphorus atoms, a commonly used dopant, in a sheet of graphene, a two-dimensional sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb pattern. The phosphorus atoms end up substituting for carbon atoms in parts of that pattern, thus altering the material's electronic, optical, and other properties in ways that can be predicted if the positions of those atoms are known.
Ultimately, the goal is to move multiple atoms in complex ways. "We hope to use the electron beam to basically move these dopants, so we could make a pyramid, or some defect complex, where we can state precisely where each atom sits," Li says.
This is the first time electronically distinct dopant atoms have been manipulated in graphene. "Although we've worked with silicon impurities before, phosphorus is both potentially more interesting for its electrical and magnetic properties, but as we've now discovered, also behaves in surprisingly different ways. Each element may hold new surprises and possibilities," Susi adds.
The system requires precise control of the beam angle and energy. "Sometimes we have unwanted outcomes if we're not careful," he says. For example, sometimes a carbon atom that was intended to stay in position "just leaves," and sometimes the phosphorus atom gets locked into position in the lattice, and "then no matter how we change the beam angle, we cannot affect its position. We have to find another ball."
Theoretical framework
In addition to detailed experimental testing and observation of the effects of different angles and positions of the beams and graphene, the team also devised a theoretical basis to predict the effects, called primary knock-on space formalism, that tracks the momentum of the "soccer ball." "We did these experiments and also gave a theoretical framework on how to control this process," Li says.
The cascade of effects that results from the initial beam takes place over multiple time scales, Li says, which made the observations and analysis tricky to carry out. The actual initial collision of the relativistic electron (moving at about 45 percent of the speed of light) with an atom takes place on a scale of zeptoseconds -- trillionths of a billionth of a second -- but the resulting movement and collisions of atoms in the lattice unfolds over time scales of picoseconds or longer -- billions of times longer.
Dopant atoms such as phosphorus have a nonzero nuclear spin, which is a key property needed for quantum-based devices because that spin state is easily affected by elements of its environment such as magnetic fields. So the ability to place these atoms precisely, in terms of both position and bonding, could be a key step toward developing quantum information processing or sensing devices, Li says.
###
Besides the leading MIT team, the international collaboration included researchers from the University of Vienna, the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Aarhus University in Denmark, National Polytechnical School in Ecuador, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and Sichuan University in China. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Army Research Office through MIT's Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies, the Austrian Science Fund, the European Research Council, the Danish Council for Independent Research, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the U.S. Department of Energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
617-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Nanofabrication
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Quantum Computing
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








