Home > Press > Graphene origami as a mechanically tunable plasmonic structure for infrared detection
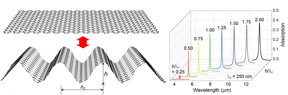 |
| Mechanically tunable light absorption wavelength with wrinkled graphene structures. A schematic illustration of the uniaxially wrinkled graphene structure (left panel) showing a reversible mechanical change of the wrinkled structure. Optical absorption spectra (right panel) for the wrinkled graphene structures with various aspect ratio of wrinkle height (h) to wavelength (λc) CREDIT University of Illinois College of Engineering |
Abstract:
Soldiers often need to see through smoke, fog, dust or any other airborne obscurant and detect the presence of toxins or other chemicals in the field or on the front lines. To identify those chemicals, they use infrared (IR) sensors and spectroscopy, which allow a specific color of light to shine at a particular frequency corresponding to each chemical. Identifying each chemical will require a soldier to coat the goggle with a unique filter, enabling the chemical signature to come through at a specific frequency (i.e., a specific color).
Graphene origami as a mechanically tunable plasmonic structure for infrared detection
Urbana, IL | Posted on April 25th, 2018Researchers at the University of Illinois, however, have successfully developed a tunable infrared filter made from graphene, which would allow a solider to change the frequency of a filter simply by controlled mechanical deformation of the filter (i.e., graphene origami), and not by replacing the substance on the goggles used to filter a particular spectrum of colors.
The research is funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, which is interested in sensors that are not only sensitive to different IR wavelengths, but also mechanically controllable and tunable. The results are published in a paper titled "Mechanically Reconfigurable Architectured Graphene for Tunable Plasmonic Resonances" in Light: Science & Applications.
This application is another in a series of discoveries of "wonder material" graphene by SungWoo Nam, an Assistant Professor of Mechanical Science and Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
"Typically when you place graphene on a substrate, it is extremely transparent and absorbs only about three percent of light," Nam noted. "At certain angles, you can see it. We use this versatility to make other structures like flexible and transparent sensors out of graphene."
Because it's one-atom thin, graphene is normally used while flat. Nam's research team asked a question: what would happen if through origami (paper-folding art), you wrinkled the graphene? Could you change the properties of graphene by altering its topography?
According to Nam, scientists haven't tried this idea before with other conventional materials because they are brittle and not able to be bent without breaking. What's unique about graphene is that it is not only thin, but it is resilient, meaning it doesn't break easily when it is bent.
"Let's say we create graphene wrinkles by mechanical deformation," Nam said. "If you get a certain dimension, is there going be any changes in the way the light is going to be absorbed by the graphene? We wanted to link the dimensions of the wrinkled graphene to its optical absorption."
Nam's team discovered that indeed, wrinkled graphene absorbs light differently depending on the structure and dimensions through plasmonic resonances, thus producing different colors. In addition, unlike paper, which can't easily be flattened after folding or crumpling, graphene can be re-stretched to become flat and wrinkle free again. Not only that but the amount of light absorption can be altered by a factor of approximately 10.
"By changing the shape, you can absorb the light of a different frequency by controlling plasmonic resonance conditions," Pilgyu Kang, the first author of the paper and now an Assistant Professor at Mechanical Engineering Department at George Mason University, stated. "And by mechanically controlling the height and wavelength of the graphene wrinkles, I can excite different surface plasmons and thus absorb different frequency. At the end of the day, you get a tunable filter."
By choosing graphene as a filter for infrared goggles, the user can turn a knob to mechanically stretch and compress the graphene. That allows for a change of the light wavelength being absorbed. So as an example of its application, a solider can thus easily tune the graphene filter to a desired wavelength to match the type of chemical he/she is looking for.
"In a conventional filter, once you make the filter, you are done," Nam concluded. "No matter the size, there is one unique light wavelength. With graphene, depending on how much you stretch and release, you can communicate in different light wavelengths."
###
This work is based on an international collaboration with Dr. Kyoung-Ho Kim and Professor Hong-Gyu Park at Korea University, and is supported by the AFOSR and National Science Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
SungWoo Nam
217-300-0267
Copyright © University of Illinois College of Engineering
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








