Home > Press > New exotic phenomena seen in photonic crystals: Researchers observe, for the first time, topological effects unique to an “open” system
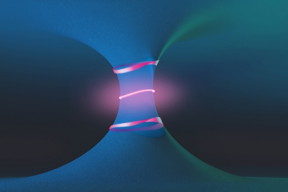 |
| A drawing illustrates the unusual topological landscape around a pair of features known as exceptional points (red dots), showing the emergence of a Fermi arc (pink line at center), and exotic polarization contours that form a Mobius-strip-like texture (top and bottom strips). Courtesy of the researchers |
Abstract:
Topological effects, such as those found in crystals whose surfaces conduct electricity while their bulk does not, have been an exciting topic of physics research in recent years and were the subject of the 2016 Nobel Prize in physics. Now, a team of researchers at MIT and elsewhere has found novel topological phenomena in a different class of systems — open systems, where energy or material can enter or be emitted, as opposed to closed systems with no such exchange with the outside.
New exotic phenomena seen in photonic crystals: Researchers observe, for the first time, topological effects unique to an “open” system
Cambridge, MA | Posted on January 12th, 2018This could open up some new realms of basic physics research, the team says, and might ultimately lead to new kinds of lasers and other technologies.
The results are being reported this week in the journal Science, in a paper by recent MIT graduate Hengyun “Harry” Zhou, MIT visiting scholar Chao Peng (a professor at Peking University), MIT graduate student Yoseob Yoon, recent MIT graduates Bo Zhen and Chia Wei Hsu, MIT Professor Marin Soljačić, the Francis Wright Davis Professor of Physics John Joannopoulos, the Haslam and Dewey Professor of Chemistry Keith Nelson, and the Lawrence C. and Sarah W. Biedenharn Career Development Assistant Professor Liang Fu.
In most research in the field of topological physical effects, Soljačić says, so-called “open” systems — in physics terms, these are known as non-Hermitian systems — were not studied much in experimental work. The complexities involved in measuring or analyzing phenomena in which energy or matter can be added or lost through radiation generally make these systems more difficult to study and analyze in a controlled fashion.
But in this work, the team used a method that made these open systems accessible, and “we found interesting topological properties in these non-Hermitian systems,” Zhou says. In particular, they found two specific kinds of effects that are distinctive topological signatures of non-Hermitian systems. One of these is a kind of band feature they refer to as a bulk Fermi arc, and the other is an unusual kind of changing polarization, or orientation of light waves, emitted by the photonic crystal used for the study.
Photonic crystals are materials in which billions of very precisely shaped and oriented tiny holes are made, causing light to interact in unusual ways with the material. Such crystals have been actively studied for the exotic interactions they induce between light and matter, which hold the potential for new kinds of light-based computing systems or light-emitting devices. But while much of this research has been done using closed, Hermitian systems, most of the potential real-world applications involve open systems, so the new observations made by this team could open up whole new areas of research, the researchers say.
Fermi arcs, one of the unique phenomena the team found, defy the common intuition that energy contours are necessarily closed curves. They have been observed before in closed systems, but in those systems they always form on the two-dimensional surfaces of a three-dimensional system. In the new work, for the first time, the researchers found a Fermi arc that resides in the bulk of a system. This bulk Fermi arc connects two points in the emission directions, which are known as exceptional points — another characteristic of open topological systems.
The other phenomenon they observed consists of a field of light in which the polarization changes according to the emission direction, gradually forming a half-twist as one follows the direction along a loop and returns back to the starting point. “As you go around this crystal, the polarization of the light actually flips,” Zhou says.
This half-twist is analogous to a Möbius strip, he explains, in which a strip of paper is twisted a half-turn before connecting it to its other end, creating a band that has only one side. This Möbius-like twist in light polarization, Zhen says, could in theory lead to new ways of increasing the amount of data that could be sent through fiber-optic links.
The new work is “mostly of scientific interest, rather than technological,” Soljačić says. Zhen adds that “now we have this very interesting technique to probe the properties of non-Hermitian systems.” But there is also a possibility that the work may ultimately lead to new devices, including new kinds of lasers or light-emitting devices, they say.
The new findings were made possible by earlier research by many of the same team members, in which they found a way to use light scattered from a photonic crystal to produce direct images that reveal the energy contours of the material, rather than having to calculate those contours indirectly.
“We had a hunch” that such half-twist behavior was possible and could be “quite interesting,” Soljačić says, but actually finding it required “quite a bit of searching to figure out, how do we make it happen?”
The work was supported by the Army Research Office through the Institute for Soldier Nanotechnologies; S3TEC, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy; the U.S. Air Force; and the National Science Foundation.
###
Written by David L. Chandler
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ms. Karl-Lydie Jean-Baptiste
MIT News Office
617-253-1682
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() PAPER: Observation of bulk Fermi arc and polarization half charge from paired exceptional points:
PAPER: Observation of bulk Fermi arc and polarization half charge from paired exceptional points:
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








