Home > Press > Researchers fabricate high performance Cu(OH)2 supercapacitor electrodes
 |
| This is a schematic description of the non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) membrane casting in the presence of an amphiphilic responsive copolymer additive. CREDIT TECHNOLOGY |
Abstract:
A team of researchers from Tufts University in Medford, MA have put together a review article, which discusses recent developments in stimuli-responsive membranes with an emphasis on membranes manufactured by polymer self-assembly. The article describes the state-of-art stimuli-responsive mem-brane manufacturing processes followed by examples explaining their stimuli-responsive behaviors. In the end, an overview of future development and challenges in this field is highlighted. The subject covered by the review article is a new and promising field. The report appears in the December 2016 issue of the journal TECHNOLOGY.
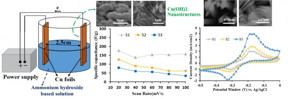
Researchers fabricate high performance Cu(OH)2 supercapacitor electrodes
Singapore | Posted on December 29th, 2016Today, the most common method of manufacture for most ultrafiltration (UF) membranes is the non-solvent induced phase separation (NIPS) process. In NIPS, a polymer solution is cast on a solid substrate, and then immersed in a coagulation bath filled with a non-solvent or a mixture of non-solvents (Figure 1). The non-solvent in coagulation bath diffuses into the polymeric solution and the solvent in polymeric solution diffuses into the non-solvent bath, which essentially is an exchange between the solvents called the demixing process. UF membranes with their nanometer-scale pores allow for the size-based separation of different components. Yet, all NIPS-prepared membranes with a mesoporous skin display a fairly broad pore size distribution in their selective layer, which is a bottleneck in selectivity for size-based separations.
Polymer self-assembly, where polymer chemistry and physics act in concert to create well-defined nanometer-scale features that can act as pores, offers the benefit of improved size-based selectivity. Several researchers have investigated processes that are scalable and compatible with the conventional NIPS process that take advantage of this.
Membrane preparation by NIPS using stimuli-responsive polymers, copolymers, and polymer-additive mixtures is an attractive approach in developing responsive membranes. The conformation/polarity/reactivity of responsive polymers or functional groups integrated in the pore structure changes in response to the stimuli they are designed for, enabling their use in systems or devices that require switchable on-demand material properties Based on the particular behavior and application, polymers can be custom-designed to respond to different external stimuli such as temperature, pH, magnetic or electric fields, ionic strength, added saccharides, antigen binding, or light. Furthermore, mem-branes that respond to multiple types of stimuli can be developed by incorporation of different stimuli-responsive functionalities in the polymer, to respond, e.g., to both pH and temperature.
Corresponding author for this study in TECHNOLOGY is Professor Ayse Asatekin, Ph.D., Other co-authors are Papatya Kaner, Prity Bengani-Lutz, and Ilin Sadeghi, all from the Smart Polymers, Membranes and Separations Laboratory at Tufts University.
####
About World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research, professional and educational communities. The company publishes about 600 books annually and about 130 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organisations like the Nobel Foundation, US National Academies Press, as well as its subsidiary, the Imperial College Press, amongst others, to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit www.worldscientific.com.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
CHEW Mun Kit
65-646-65775
Copyright © World Scientific
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Self Assembly
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
![]() Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








