Home > Press > Subatomic microscopy key to building new classes of materials
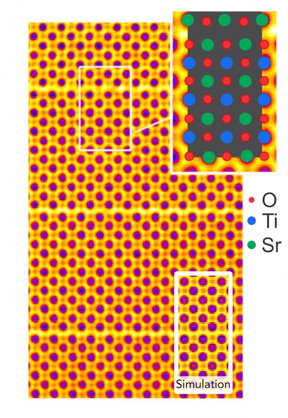 |
| Colorized sub-Angstrom scanning transmission electron microscope image clearly shows individual atomic columns of strontium (green), titanium (blue), and oxygen (red). A simulated image is overlaid showing close agreement between theory and experiment. The brick and mortar structure is visible. CREDIT: Greg Stone/Penn State |
Abstract:
Researchers at Penn State and the Molecular Foundry at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory are pushing the limits of electron microscopy into the tens of picometer scale, a fraction of the size of a hydrogen atom.
Subatomic microscopy key to building new classes of materials
University Park, PA | Posted on September 1st, 2016The ability to see at this subatomic level is crucial for designing new materials with unprecedented properties, such as materials that transition from metals to semiconductors or that exhibit superconductivity. The researchers' work describing the first atomic scale evidence for strain-induced ferroelectricity in a layered oxide appears online today, (Aug. 31), in Nature Communications.
"This paper is important because it highlights our ability to design new classes of materials that can be tuned, one atomic layer at a time, to get interesting new properties such as high-frequency tunable dielectrics, which are of interest to the semiconductor industry," said first author Greg Stone, a former Penn State post-doctoral scholar now at the U.S. Army Research, Development, and Engineering Center.
Designing new materials with potentially useful properties requires the close collaboration of theory, synthesis and characterization - the first to build the mathematical models needed, the second to create the material in the lab, and the third to visualize and measure the material's properties and provide feedback to tweak theories and improve synthesis.
This study builds on previous theoretical work by coauthors Turan Birol and Craig Fennie of Cornell University and experimental work by coauthors Venkatraman Gopalan of Penn State and Darrell Schlom, formerly at Penn State and now at Cornell, and their students. Gopalan and Nasim Alem, professors of materials science and engineering at Penn State, led the current study.
"The material we are looking at is a form of strontium titanate called a layered oxide," said Gopalan. "This study brings together electron microscopy and density functional theory on a 5 to 10 picometer length scale to show why these materials are such good tunable dielectrics. The key is phase competition, and for the first time, we show that many polar phases with similar energies compete in this material on the atomic scale, just as theory predicted, which gives it large tunability under a voltage."
Complex oxides are materials that form by combining negatively charged oxygen and two other positively charged ions. In this instance, the team examined strontium titanate with a structure called Ruddlesden-Popper (RP), after the two scientists who discovered it. The structure looks like a brick and mortar wall, with the bricks made of the strontium titanate and the thin mortar between the bricks made up of strontium oxide. When the bricks are layered in this fashion, new properties emerge that would not appear in a single brick.
"In the case of RP-strontium titanate, the emergent property is ferroelectricity, which means it has a built-in electrical polarization within its structure," said Gopalan. "But it could be magnetism or metal-insulator transitions or superconductivity, depending on the atoms involved and the layering order of the materials."
Because each layer of brick has a weak connection to other layers, the material can have competing states, with one layer polarized in a direction opposite to a neighboring layer. These competing states result in a material with a strong response to a small external stimulus, such as an electric or magnetic field or temperature. In the case of strontium titanate, there is a large dielectric response, which is the ability to store large amounts of energy, as in a capacitor.
Cell phones have many dielectric components that are very small and have to hold a charge. As cell phones transition from 4G networks to 5G, which means they are processing at 5 billion cycles per second, better materials that respond at higher frequencies are crucial. RP-strontium titanate is a material that is definitely superior to current materials.
Colin Ophus of the National Center for Electron Microscopy facility of the Molecular Foundry, said, "This work is an excellent example of the materials advances possible when we close the feedback loop between first principles calculations and atomic resolution electron microscopy."
His colleague Jim Ciston at the Molecular Foundry adds, "The precision of the agreement between theory and experiment is critical to unraveling the subtle differences in structure between competing ferroelectric phases. These images of atomic positions are more than pretty pictures of remarkable precision, but contain an enormous amount of quantifiable information about the minute distortions in atomic positions that can lead to surprising properties."
###
Additional coauthors on the paper, titled "Atomic Scale Imaging of Competing Polar States in a Ruddleston-Popper Layered Oxide," were Nasim Alem, assistant professor of materials science and engineering, Penn State, Turan Birol, Fennie's Ph.D. student now assistant professor at University of Minnesota, Che-Hui Lee, Schlom's Ph.D. student at Penn State and Cornell, and Penn State staff scientist Ke Wang.
Support was provided through the Penn State Center for Nanoscale Science, a National Science Foundation Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC), the Department of Energy and the Rutgers Center for Materials Theory. Work at the Molecular Foundry was supported by the Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, of the U. S. Department of Energy. Portions of the work were performed in the Penn State electron microscopy facilities in Penn State's Materials Research Institute.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-9481
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Superconductivity
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








