Home > Press > Radiation-guided nanoparticles zero in on metastatic cancer
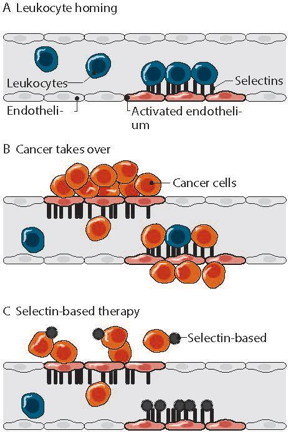 |
| This is a schematic illustration of selectins' role in inflammation (A) and cancer progression (B). This mechanism can be used for selectin-based targeted therapy (C). This material relates to a paper that appeared in the June 29, 2016 issue of Science Translational Medicine, published by AAAS. The paper, by Y. Shamay at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, NY, and colleagues was titled, "P-selectin is a nanotherapeutic delivery target in the tumor microenvironment." CREDIT: Kedmi et al., Science Translational Medicine (2016) |
Abstract:
Zap a tumor with radiation to trigger expression of a molecule, then attack that molecule with a drug-loaded nanoparticle. That's the approach researchers working in mice have taken in a new study that aims to make delivery of chemotherapy to metastatic tumors more effective.
Radiation-guided nanoparticles zero in on metastatic cancer
Washington, DC | Posted on July 1st, 2016The researchers say that the radiation-guided nanoparticles may offer a new approach for penetrating the vascular barrier that often thwarts current nanomedicines from reaching metastatic tumors. To spread to distant organs, cancer cells in the bloodstream latch onto adhesion molecules known as P-selectins in the blood vessel walls. Yosi Shamay and colleagues further found that unlike normal tissues, many human cancers--including lung, ovarian, breast, and liver--overexpress P-selectin on tumor cells and in surrounding blood vessels. To exploit this molecule as a therapeutic target, the researchers designed nanoparticle drug carriers composed of fucoidan, a seaweed-derived compound that naturally binds to P-selectin. In a mouse model of lung cancer and metastatic melanoma and breast tumors, all of which express P-selectin, the nanoparticles selectively delivered chemotherapy drugs to the tumors, improving tumor reduction and overall survival better than did the free form of the drugs or drug-loaded nanoparticles not made of fucoidan. For tumors that do not normally express P-selectin, Shamay et al. used radiation, which is known to boost P-selectin expression in tissues, to guide the nanoparticles to the tumor site. When combined with radiation, the nanotherapy effectively shrunk lung tumors lacking P-selectin in mice. In a related Focus, Ranit Kedmi and Dan Peer discuss the promises and challenges of moving the nanotherapy to the clinic. Radiation-guided nanoparticles may offer a new tool for delivering drugs to almost any tumor, they note, but further development would need to address the double-edged sword of radiation's potential to trigger P-selectin expression that might unintentionally promote cancer spread.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Science Press Package Team
202-326-6440
Copyright © American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Cancer
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








