Home > Press > Nanocars taken for a rough ride: Rice, NC State researchers test single-molecule cars in open air
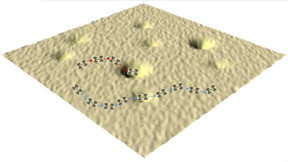 |
| Molecules that alight on a surface used to test nanocars look more like obstacles, according to researchers at Rice University and North Carolina State University testing the mobility of single-molecule cars in open air. Credit: Rice/North Carolina State |
Abstract:
If you're driving a nanocar on the open road, things are bound to get sticky.
Rice University researchers who developed the first nanocars and colleagues at North Carolina State University found in recent tests that driving their vehicles in ambient conditions – exposed to open air, rather than a vacuum – got dicey after a time because the hydrophobic single-molecule cars stuck to the "road" and created what amounted to large speed bumps.
Nanocars taken for a rough ride: Rice, NC State researchers test single-molecule cars in open air
Houston, TX | Posted on June 1st, 2016The findings were reported in the American Chemical Society's Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
The work by Rice chemist James Tour, NC State analytical chemist Gufeng Wang and their colleagues came as Rice prepares to take part in the first NanoCar Race in Toulouse, France, in October. Rice researchers are members of one of five international teams that plan to enter the competition.
Just like in the macro world, driving conditions are important for moving nanocars. Though the race will be run in an ultra-cold vacuum, the Rice researchers thought it wise to study how their latest model of nanocars would fare in a more natural setting.
"Our long-term goal is to make nanomachines that operate in ambient environments," Tour said. "That's when they will show potential to become useful tools for medicine and bottom-up manufacturing."
The newest generation of Rice nanocars features adamantane wheels that are slightly hydrophobic (water-repellent). Tour said some hydrophobicity is important to help keep the nanocars attached to a surface, but if the tires are too hydrophobic, the cars could become permanently immobilized. That is because hydrophobic things tend to stick together to minimize the amount of surface area that is in contact with water. Things that are hydrophilic, or water-liking, are more amenable to floating freely in water, Tour said.
In the latest Rice tests with the new tires, the nanocars were placed on surfaces that were either clean glass or glass coated with the polymer polyethylene glycol (PEG). Glass is the most frequently used substrate in nanocar research. Tour said the PEG-coated glass slides were used for their anti-fouling – nonsticky – properties, while the clean glass slides were treated with hydrogen peroxide so the hydrophobic wheels wouldn't stick.
He said the cars weren't so much being driven as undergoing "directed diffusion" in the tests. The point, he said, was to establish the kinetics of nanocar movement and understand the potential energy surface interaction between the car and surface over time.
"We want to know what makes a nanocar 'hit the brakes' and how much external energy we need to apply to start it moving again," he said.
The researchers let their cars run freely on a solid surface exposed to the air and tracked their movements by exciting embedded fluorescent tags.
The cars that moved via Brownian diffusion slowed down during the 24 hours that the slides were under observation. Tour said slides absorbed molecules from the air; as more and more of these molecules stuck to the surface, the slides become progressively more "dirty" throughout the experiment. Each nanocar is a single, complex molecule that contains just a few hundred atoms, so any other molecules they encounter on the roadway are huge obstacles that act like sticky foam. Each collision with one of these obstructions makes the nanocar slow down, and eventually the cars become permanently stuck.
Wang said that from an energy perspective -- that is, the energetic relationship between the molecular cars and those that make up the road -- molecules adsorbed from air generate many potential energy wells, just like puddles on the potential energy surface. These puddles can slow or permanently trap the nanocars.
Tests showed that nearly twice as many of the cars appeared to move on the nonsticking PEG slides, and all moved a little faster than those on the bare glass.
The researchers noted that they could not view the new models with scanning tunneling microscopes because those only work in a vacuum and they emit energy that could influence movement of the cars. For this reason, the researchers tagged each nanocar with a fluorescent marker and used confocal microscopes to track the cars' movements.
Co-authors of the paper are graduate students Victor Garcia-López and Pin-Lei Chu of Rice and graduate students Fang Chen and Tao Jin and postdoctoral scholar Bhanu Neupane of North Carolina State. Wang is an assistant professor of analytical chemistry at North Carolina State. Tour is the T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of computer science and of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice.
The National Science Foundation and North Carolina State University supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Nanotech scientists create world's smallest origami bird March 17th, 2021
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








