Home > Press > Tiny tubes move into the fast lane
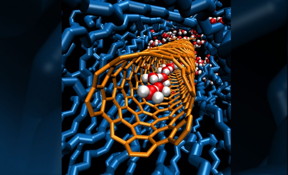 |
| A single chain of water molecules lines the cavity inside a carbon nanotube porin, which is embedded in a lipid bilayer. Image by: Y. Zhang and Alex Noy/LLNL. |
Abstract:
For the first time, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) researchers have shown that carbon nanotubes as small as eight-tenths of a nanometer in diameter can transport protons faster than bulk water, by an order of magnitude.
Tiny tubes move into the fast lane
Livermore, CA | Posted on April 5th, 2016The research validates a 200-year old mechanism of proton transport.
A nanometer is one billionth of a meter. By comparison, the diameter of a human hair is 20,000 nanometers.
The transport rates in these nanotube pores, which form one-dimensional water wires, also exceed those of biological channels and man-made proton conductors, making carbon nanotubes the fastest known proton conductor. The research appears in the April 4 advanced online edition of the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
Practical applications include proton exchange membranes, proton-based signaling in biological systems and the emerging field of proton bioelectronics (protonics).
"The cool thing about our results is that we found that when you squeeze water into the nanotube, protons move through that water even faster than through normal (bulk) water," said Aleksandr Noy, an LLNL biophysicist and a lead author of the paper. (Bulk water is similar to what you would find in a cup of water that is much bigger than the size of a single water molecule).
The idea that protons travel fast in solutions by hopping along chains of hydrogen-bonded water molecules dates back 200 years to the work of Theodore von Grotthuss and still remains the foundation of the scientific understanding of proton transport. In the new research, LLNL researchers used carbon nanotube pores to line up water molecules into perfect one-dimensional chains and showed that they allow proton transport rates to approach the ultimate limits for the Grotthuss transport mechanism.
"The possibility to achieve fast proton transport by changing the degree of water confinement is exciting," Noy said. "So far, the man-made proton conductors, such as polymer Nafion, use a different principle to enhance the proton transport. We have mimicked the way biological systems enhance the proton transport, took it to the extreme, and now our system realizes the ultimate limit of proton conductivity in a nanopore."
Of all man-made materials, the narrow hydrophobic inner pores of carbon nanotubes (CNT) hold the most promise to deliver the level of confinement and weak interactions with water molecules that facilitate the formation of one-dimensional hydrogen-bonded water chains that enhance proton transport.
Earlier molecular dynamic simulations showed that water in 0.8 nm diameter carbon nanotubes would create such water wires and predicted that these channels would exhibit proton transport rates that would be much faster than those of bulk water. Ramya Tunuguntla, an LLNL postdoctoral researcher and the first author on the paper, said that despite significant efforts in carbon nanotube transport studies, these predictions proved to be hard to validate, mainly because of the difficulties in creating sub-1-nm diameter CNT pores.
However, the Lawrence Livermore team along with colleagues from the Lawrence Berkeley National Lab and UC Berkeley was able to create a simple and versatile experimental system for studying transport in ultra-narrow CNT pores. They used carbon nanotube porins (CNTPs), a technology they developed earlier at LLNL, which uses carbon nanotubes embedded in the lipid membrane to mimic biological ion channel functionality. The key breakthrough was the creation of nanotube porins with a diameter of less than 1 nm, which allowed researchers for the first time to achieve true one-dimensional water confinement.
###
Other Livermore and Berkeley researchers include Frances Allen, Kyunghoon Kim and Allison Belliveau. The work was funded by the Department of Energy's Office of Basic Energy Sciences.
####
About Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is a national security laboratory, with a mission to ensure national security and apply science and technology to the important issues of our time. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anne Stark
925-422-9799
Copyright © Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








