Home > Press > Nanotechnology for label-free colorimetric detection of c-myc mRNA oncogene
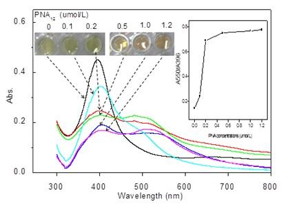 |
| Depicts visual colors of AgNP solutions (0.45 nmol/L) incubated with different PNA12 concentrations (0-1.2 μmol/L) and absorption spectra of corresponding solutions.
©Science China Press |
Abstract:
Given the important role in functioning as oncogenes or tumor suppressors, c-myc mRNA has emerged as a potential biomarker for cancer detection. In particular, abnormal expression of mRNAs is commonly observed at early stages of colon cancer development. Therefore, sensitive detection of c-myc mRNA has become a promising approach to achieving early clinical diagnosis of cancer and paves the way for precision medicine. Recently, a China-U.S. collaborative research team reported a label-free colorimetric protocol based on peptide nucleic acid/silver nanoparticles (PNA/AgNPs) for specific detection of c-myc mRNA biomarkers. A correlated research article entitled "A label-free colorimetric assay for detection of c-myc mRNA based on peptide nucleic acid and silver nanoparticles" was recently published in the journal of Science Bulletin (2016, vol.61, No. 4: 276-281, Springer), written by Dr. Xia Li from Liaocheng University (Shandong, China), Shandong Taishan Scholar Prof. Jifeng Liu (current, Tianjin Science and Technology University) and Prof. Chenzhong Li at the Florida International University (Miami, USA).
Nanotechnology for label-free colorimetric detection of c-myc mRNA oncogene
Beijing, China | Posted on March 23rd, 2016PNA has the same hydrogen-bonding nucleobases as DNA, but is attached to an uncharged N-(2-aminoethyl) glycine backbone which confers superior target-binding characteristics and physicochemical robustness over native DNA probes. PNA can induce AgNPs aggregations effectively, which reduces the optical absorbance and leads to a significant color change from yellow to red-brown (Fig.1). Interestingly, the aggregation of AgNPs can be reversibly controlled by the formation of PND-mRNA complexes by adding c-myc mRNA to the complementary PNS probe-containing solution. The reversible dissociation process could be easily observed by monitoring the color change from red-brown to yellow by the naked eye (Fig.2).
The fundamental mechanism of AgNPs-PNA interaction is also investigated at a molecular level. From studying the most probable configurations of PNA structure on AgNPs by molecular modeling, the team found that multiple hydrogen bonds can be formed between PNA on AgNPs, resulting in AgNPs naturally aggregating with one another. Additionally, the reduced electrostatic repulsion has also been considered as another factor causing the PNA-induced AgNPs aggregation. In the presence of target c-myc mRNA, the PNA prefers to switch its configuration to combine with the complementary mRNA target, resulting in disaggregation of AgNPs into dispersed Ag nanoparticles. "This PNA and AgNPs integrated technology is quite simple, specific and sensitive. We are also considering transferring the liquid-based sensing platform to solid bio-sensing devices such as through a paper or silicon-based platform. In addition, we aim to integrate the bar code technology and smart phone to develop a portable oncogene screening biosensor for point-of-care applications", said by Chenzhong Li, professor of Biomedical Engineering at Florida International University, Florida.
###
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21305058, 21205056, 21075058 and 21503104) and Tai-Shan Scholar Research Fund of Shandong Province.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chen-zhong Li
Copyright © Science China Press
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Cancer
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








