Home > Press > A new model for how twisted bundles take shape: UMass Amherst, Virginia Tech team unravel rules of twisted bundle morphology
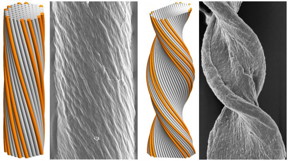 |
| Cyindrical (left) and tape-like (right) twisted filament bundles: model morphologies (simulated assemblies) and experimental observations (amyloid fibers). Greg Grason and colleagues have for the first time identified key factors that govern the final morphology of self-assembling chiral filament bundles. CREDIT: UMass Amherst/Greg Grason |
Abstract:
In the current issue of Nature Materials, polymer scientists Greg Grason, Douglas Hall and Isaac Bruss at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, with Justin Barone at Virginia Tech, identify for the first time the factors that govern the final morphology of self-assembling chiral filament bundles. They also report experimental results supporting their new model.
A new model for how twisted bundles take shape: UMass Amherst, Virginia Tech team unravel rules of twisted bundle morphology
Amherst, MA | Posted on March 21st, 2016At the molecular level, Grason explains, chiral filament bundles are many-stranded, self-twisting, yarn-like structures. One example are amyloid fibers, assemblies of misfolded proteins linked to diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Many other proteins take this shape, including collagen, the most abundant protein in the body, and sickle-hemoglobin proteins found in sickle-cell anemia. But how they attain their final size and shape has not been well understood.
Previous work by Bruss and Grason described the formation of cable-like filament bundles. When Grason presented this at Virginia Tech, Justin Barone, a biological systems engineer, approached him with a question about the geometric structure of amyloid fibers he had been studying. Barone asked why the shapes he was observing were in some cases flat and tape-like, while under other conditions they were cylindrical.
Grason recalls, "Justin's questions about the shape of amyloid fibers set us on the track to figure out how fibers form from many copies of identical filaments and know what shapes to be. Since filaments attract one another, understanding what makes fibers grow fatter is not so hard. The challenge is to understand what makes the process stop at certain sizes, and why a fiber sometimes grows larger in one direction than the other, leading to different cross-sectional shapes."
He adds, "Based on our new model, we have new design rules for controlling the size and shape of 'self-spinning' nano-fiber materials used in applications such as soft-gel scaffolds that can be deployed in filters, sensor patches or any place where you need material architectures with tunable mechanics and size scales."
In the human body, many structures are made of collagen bundles or other protein filaments, Grason explains. "The bundles in your eye are small and more uniform because the cornea has to be transparent, compared to fibers that make up your tendons, which have to be thicker and stronger. These different tissues are formed from basically the same building blocks, yet they assemble into different architectures."
He adds, "We wanted to develop a physical model of what governs the structure of protein fibers and other fiber-forming systems. How do they self-organize and what determines their size and shape? The basic ingredients are molecular-scale, nano-filaments that stick to one another, forming a structure that looks like rope or cable, made of strands that twist together."
Grason says it was already known that the "screw-like" structure of chiral filaments caused them to twist around one another in bundle assembles. What was not known, and is the focus of the current study, is how this structure along the length controls the lateral distribution of strands in the fiber. Using geometric and mathematical models combined with computational simulations, the researchers discovered that the number of strands involved is a significant predictor of how strong the final structure is and whether its protein filaments will take a cylindrical shape or the ribbon-like shape in cross section.
Grason explains that the key insight made earlier by his group was to show that filament twisting in the bundles 'frustrates' the packing between neighbor filaments, making it impossible to evenly space filaments in cross section. The upshot of this frustration is that it leads to a feedback mechanism between the twist pattern and the lateral shape of the bundle. "We now have a model that explains how the number of strands underlies morphology selection."
He adds, "A smaller number of strands allows them to keep the right distance from their neighbors, so even though there is a twist, if the twist is not too big and the strand number not too big, the structure doesn't get too crowded and keeps a cylindrical cross section. But once the number of strands gets larger, outer strands get too close for comfort and a tape-like, or twisted ribbon structure will emerge."
"For the first time, we are able to predict that the frustration will lead to new shape transitions. For relatively narrow and weakly twisted bundles, the cost of fewer contacts at the sides of the bundle favors a cylindrical shape. But above a critical size, the cost of the frustration causes the morphology to change dramatically, leading to bundle shapes that are very anisotropic, much wider in one dimension and thinner in the other."
To test their new predictions, Hall worked with Bruss, now at the University of Michigan, to develop and implement a simulation model to show how the filament twist pattern determines how large these assemblies will grow, how fat they can be and what shape their cross sections will have. In the end, they found that both simulated and experimental amyloid fibers could be classified as either cylinder-forming and tape-forming according to a relatively simple combination of molecular and geometric parameters of the assembly.
Grason says, "To start out with complex and unexplained observations, then to design the model that let others run the simulations to show it was true, then to bring it all the way back to confirm in the experimental data was particularly satisfying. It doesn't always happen this way." This work was supported by a National Science Foundation CAREER award and by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Janet Lathrop
413-545-0444
Copyright © University of Massachusetts at Amherst
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Self Assembly
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
![]() Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








