Home > Press > Iowa State engineers develop flexible skin that traps radar waves, cloaks objects
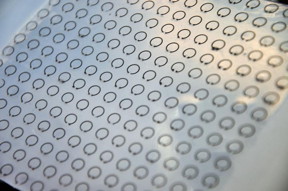 |
| This flexible, stretchable and tunable "meta-skin" can trap radar waves and cloak objects from detection. CREDIT: Liang Dong/Iowa State University |
Abstract:
Iowa State University engineers have developed a new flexible, stretchable and tunable "meta-skin" that uses rows of small, liquid-metal devices to cloak an object from the sharp eyes of radar.
Iowa State engineers develop flexible skin that traps radar waves, cloaks objects
Ames, IA | Posted on March 7th, 2016The meta-skin takes its name from metamaterials, which are composites that have properties not found in nature and that can manipulate electromagnetic waves. By stretching and flexing the polymer meta-skin, it can be tuned to reduce the reflection of a wide range of radar frequencies.
The journal Scientific Reports recently reported the discovery online. Lead authors from Iowa State's department of electrical and computer engineering are Liang Dong, associate professor; and Jiming Song, professor. Co-authors are Iowa State graduate students Siming Yang, Peng Liu and Qiugu Wang; and former Iowa State undergraduate Mingda Yang. The National Science Foundation and the China Scholarship Council have partially supported the project.
"It is believed that the present meta-skin technology will find many applications in electromagnetic frequency tuning, shielding and scattering suppression," the engineers wrote in their paper.
Dong has a background in fabricating micro and nanoscale devices and working with liquids and polymers; Song has expertise in looking for new applications of electromagnetic waves.
Working together, they were hoping to prove an idea: that electromagnetic waves - perhaps even the shorter wavelengths of visible light - can be suppressed with flexible, tunable liquid-metal technologies.
What they came up with are rows of split ring resonators embedded inside layers of silicone sheets. The electric resonators are filled with galinstan, a metal alloy that's liquid at room temperature and less toxic than other liquid metals such as mercury.
Those resonators are small rings with an outer radius of 2.5 millimeters and a thickness of half a millimeter. They have a 1 millimeter gap, essentially creating a small, curved segment of liquid wire.
The rings create electric inductors and the gaps create electric capacitors. Together they create a resonator that can trap and suppress radar waves at a certain frequency. Stretching the meta-skin changes the size of the liquid metal rings inside and changes the frequency the devices suppress.
Tests showed radar suppression was about 75 percent in the frequency range of 8 to 10 gigahertz, according to the paper. When objects are wrapped in the meta-skin, the radar waves are suppressed in all incident directions and observation angles.
"Therefore, this meta-skin technology is different from traditional stealth technologies that often only reduce the backscattering, i.e., the power reflected back to a probing radar," the engineers wrote in their paper.
As he discussed the technology, Song took a tablet computer and called up a picture of the B-2 stealth bomber. One day, he said, the meta-skin could coat the surface of the next generation of stealth aircraft.
But the researchers are hoping for even more - a cloak of invisibility.
"The long-term goal is to shrink the size of these devices," Dong said. "Then hopefully we can do this with higher-frequency electromagnetic waves such as visible or infrared light. While that would require advanced nanomanufacturing technologies and appropriate structural modifications, we think this study proves the concept of frequency tuning and broadening, and multidirectional wave suppression with skin-type metamaterials."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liang Dong
515-294-0388
Jiming Song
Electrical and Computer Engineering
515-294-8396
Mike Krapfl
News Service
515-294-4917
Copyright © Iowa State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() Under pressure - space exploration in our time: Advancing space exploration through diverse collaborations and ethical policies February 16th, 2024
Under pressure - space exploration in our time: Advancing space exploration through diverse collaborations and ethical policies February 16th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() Manufacturing advances bring material back in vogue January 20th, 2023
Manufacturing advances bring material back in vogue January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








