Home > Press > Nanotechnology delivery system offers new approach to skin disease therapies: Hebrew University formula that activates the body's natural defense against free radicals could control a variety of skin pathologies and disorders
 |
| These are the consequences of skin exposure to stressors. CREDIT: Maya Ben-Yehuda Greenwald |
Abstract:
Researchers at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem have developed a nanotechnology-based delivery system containing a protective cellular pathway inducer that activates the body's natural defense against free radicals efficiently, a development that could control a variety of skin pathologies and disorders.
Nanotechnology delivery system offers new approach to skin disease therapies: Hebrew University formula that activates the body's natural defense against free radicals could control a variety of skin pathologies and disorders
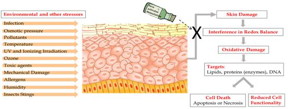
Jerusalem, Israel | Posted on March 2nd, 2016The human skin is constantly exposed to various pollutants, UV rays, radiation and other stressors that exist in our day-to-day environment. When they filter into the body they can create Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) - oxygen molecules known as Free Radicals, which are able to damage and destroy cells, including lipids, proteins and DNA.
In the skin - the largest organ of the body - an excess of ROS can lead to various skin conditions, including inflammatory diseases, pigmenting disorders, wrinkles and some types of skin cancer, and can also affect internal organs. This damage is known as Oxidative Stress.
The body is naturally equipped with defense mechanisms to counter oxidative stress. It has anti-oxidants and, more importantly, anti-oxidant enzymes that attack the ROS before they cause damage.
In a review article published in the journal Cosmetics, a PhD student from The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, working in collaboration with researchers at the Technion - Israel Institute of Technology, suggested an innovative way to invigorate the body to produce antioxidant enzymes, while maintaining skin cell redox balance - a gentle equilibrium between Reactive Oxygen Species and their detoxification.
"The approach of using the body's own defense system is very effective. We showed that activation of the body's defense system with the aid of a unique delivery system is feasible, and may leverage dermal cure," said Hebrew University researcher Maya Ben-Yehuda Greenwald.
Ben-Yehuda Greenwald showed that applying nano-size droplets of microemulsion liquids containing a cellular protective pathway inducer into the skin activates the natural skin defense systems.
"Currently, there are many scientific studies supporting the activation of the body's defense mechanisms. However, none of these studies has demonstrated the use of a nanotechnology-based delivery system to do so," Ben-Yehuda Greenwald said.
Production of antioxidant enzymes in the body is signaled in the DNA by activation of Nrf2 - a powerful protein that exists in every cell in our body. This Nrf2 cellular-protective signaling pathway is a major intersection of many other signaling pathways affecting each other and determining cell functionality and fate. Nrf2 is capable of coordinating the cellular response to internal as well as external stressors by tight regulation of phase-II protective enzymes, such as the antioxidant enzymes.
Ben-Yehuda Greenwald has also discovered a new family of compounds capable of activating the Nrf2 pathway. Moreover, by incorporating them into the unique delivery system she has developed, she managed to efficiently stimulate the activation of the Nrf2 pathway and mimic the activity of the body's' natural way of coping with a variety of stress conditions.
"The formula we have created could be used in topical medication for treating skin conditions. Our formula could be used both as preventive means and for treatment of various skin conditions, such as infections, over-exposure to UV irradiation, inflammatory conditions, and also internal disease," she said.
While the researchers focused on the skin, the formulation could prove to be effective in enhancing the body's natural protection against the damaging effects of ROS in other parts of the body, such as inflammation in cardiovascular diseases, heart attack, cancer, multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's.
###
Ben-Yehuda Greenwald integrated several fields of research into her work and was guided by experts in their fields - Prof. Roni Kohen, the Director of the School of Pharmacy, The Institute of Drug Research in the Hebrew University's Faculty of Medicine; Prof. Shmuel Ben-Sasson from the Department of Developmental Biology and Cancer Research at The Institute for Medical Research Israel-Canada in the Hebrew University's Faculty of Medicine; and Prof. Havazelet Bianco-Peled from the Department of Chemical Engineering at the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology.
She conducted her study at the David and Ines Myers Skin Research Laboratory at The Institute for Drug Research in the School of Pharmacy at The Hebrew University's Faculty of Medicine.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Avivit Delgoshen
972-258-82904
Copyright © The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Cancer
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Super-efficient laser light-induced detection of cancer cell-derived nanoparticles: Skipping ultracentrifugation, detection time reduced from hours to minutes! October 6th, 2023
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








