Home > Press > Nanoparticles on nanosteps: A new study reduces wastage and increases the efficiency of catalysts
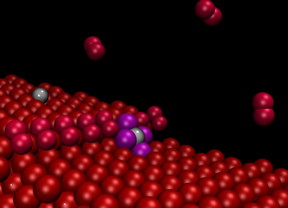 |
| These are platinum nanoparticles on nanosteps. CREDIT: SISSA/CNR-IOM |
Abstract:
Platinum is one of the costly metals used as catalysts in new technologies employed for industrial chemical processes, renewable energy sources, pollution control and many other purposes. In particular, it is used for fuel cells, devices that turn chemical energy directly into electrical energy, without combustion. Research has shown that the greatest efficiency is achieved when the catalyst is available in the form of nanoparticles (smaller than 10-9 m). Simply put, the greater the dispersion of the material and the smaller the size of the particles, the more is it available for catalysis. Unfortunately, the laws of thermodynamics cause the particles to "stick" to one another and form larger clusters, which is why the material becomes less effective over time. So what can be done to maintain maximal dispersion of the "nanopowder"?
Nanoparticles on nanosteps: A new study reduces wastage and increases the efficiency of catalysts
Trieste, Italy | Posted on March 2nd, 2016A group of SISSA/CNR IOM scientists (with the collaboration of the Univerzita Karlova in Prague) has studied a way to produce tiny platinum grains consisting of one atom only and to keep them dispersed in a stable manner, by exploiting the properties of the substrate on which they rest.
"Theoretical work demonstrated that irregularities in the surface known as steps and observed in experiments conducted at the Trieste Synchrotron tend to attract and separate the nanoparticles, causing them to remain literally attached in the form of single atoms", explains Stefano Fabris, CNR-IOM/SISSA research fellow.
"The particles adhering to the steps were no longer visible even using an atomic resolution microscope" explains Nguyen-Dung Tran, a SISSA PhD student. "However, their presence was detected by spectroscopy, so they were indeed there, but they were no longer visible or free to move around". "Our computer simulations solved this dilemma, showing that the particles on the steps are reduced to single atoms" adds Matteo Farnesi Camellone (CNR-IOM), another author of the study.
"If the surface is engineered to contain a large number of these defects, then the force that binds the particles to the substrate effectively offsets the aggregation force", explains Fabris. The theoretical work, led by Fabris, allowed the researchers to develop a "system model" on the computer able predict the behaviour of the material. The model's predictions were confirmed by the experimental measurements. Materials like this can be used for fuel cell electrodes, with far lower costs than the current ones.
"Reducing the amount of platinum used in fuel cell electrodes is a priority, not only to contain costs but also to ensure environmental sustainability, as also indicated by the recent European directives" concludes Fabris. The European project ChipCAT, which funded this research, aims precisely to achieve this goal.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Federica Sgorbissa
39-040-378-7644
Copyright © International School for Advanced Studies (SISSA)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Fuel Cells
![]() Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
Current and Future Developments in Nanomaterials and Carbon Nanotubes: Applications of Nanomaterials in Energy Storage and Electronics October 28th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








