Home > Press > Breakthrough enables ultra-fast transport of electrical charges in polymers
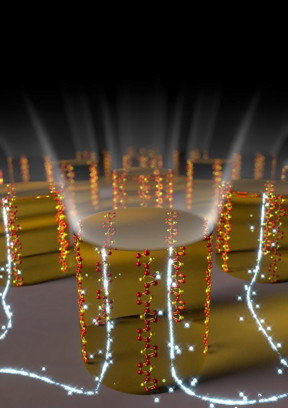 |
| Vertically aligned chains in the organic semiconducting polymer inside microscopic patterns. CREDIT: Umeċ University |
Abstract:
A research team at Umeċ University in Sweden has showed, for the first time, that a very efficient vertical charge transport in semiconducting polymers is possible by controlled chain and crystallite orientation. These pioneering results, which enhance charge transport in polymers by more than 1,000 times, have implications for organic opto-electronic devices and were recently published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Breakthrough enables ultra-fast transport of electrical charges in polymers
Umeċ, Sweden | Posted on January 30th, 2016Conjugated semiconducting polymers (plastic) possess exceptional optical and electronic properties, which make them highly attractive in the production of organic opto-electronic devices, such as for instance photovoltaic solar cells (OPV), light emitting diodes (OLED) and lasers.
Polythiophene polymers, such as poly(3-hexylthiophene), P3HT, have been among the most studied semiconducting polymers due to their strong optical absorbance and ease of processing into a thin film from solution. In both OPVs and OLEDs, charges must be transported in the out of plane (vertical) direction inside the polymer film.
However, until now the vertical charge carrier mobility of organic semiconductors, i.e. the ability of charges to move inside the material, has been too low to produce fast charge transport in electronic devices. Faster charge transport can occur along the polymer chain backbone. However, a method to produce controlled chain orientation and high mobility in the vertical direction has remained elusive until now.
In the present work, a team of chemists and materials scientists, led by Professor David R. Barbero at Umeċ University, has found a new method to align chains vertically and to produce efficient transport of electric charges through the chain backbone. In this new study, moreover, high charge transport and high mobility were obtained without any chemical doping, which is often used to artificially enhance charge transport in polymers.
"The transport of electric charge is greatly enhanced solely by controlled chain and crystallite orientation inside the film. The mobility measured was approximately one thousand times higher than previously reported in the same organic semiconductor," says David Barbero.
In what way will these results affect the field of organic electronics?
"We believe these results will impact the fields of polymer solar cells and organic photodiodes, where the charges are transported vertically in the device. Organic-based devices have traditionally been slower and less efficient than inorganic ones (e.g. made of silicon), in part due to the low mobility of organic (plastic) semiconductors. Typically, plastic semiconductors, which are only semi-crystalline, have hole mobilities about 10,000 times lower than doped silicon, which is used in many electronic devices. Now we show it is possible to obtain much higher mobility, and much closer to that of silicon, by controlled vertical chain alignment, and without doping," says David Barbero.
The charge transport was measured using nanoscopic electrical measurements, and gave a mobility averaging 3.1 cm2/V.s, which is the highest mobility ever measured in P3HT, and which comes close to a theoretical estimation of the maximum mobility in P3HT. Crystallinity and molecular packing characterisation of the polymer was performed by synchrotron X-ray diffraction at Stanford University's National Accelerator (SLAC) and confirmed that the high mobilities measured were due to the re-orientation of the polymer chains and crystallites, leading to fast charge transport along the polymer backbones.
These results, published in Advanced Materials, may open up the route to produce more efficient organic electronic devices with vertical charge transport (e.g. OPV, OLED, lasers etc.), by a simple and inexpensive method, and without requiring chemical modification of the polymer.
###
About plastics: Regular plastic materials are non-conducting, but if they contain conjugated double bonds, with delocalized electrons, which run alongside the chain backbone, they can conduct charges and transport electricity. However, these electrons (or their positive counterpart, holes) are still not as mobile as in metals or silicon, and therefore their mobility is much lower. To increase the charge mobility, the polymer is usually doped, which means introducing impurities into the material for the purpose of modulating its electrical properties.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Anna Lawrence
46-722-459-011
Copyright © Umeċ University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Organic Electronics
Laboratories
![]() A batterys hopping ions remember where theyve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a batterys electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A batterys hopping ions remember where theyve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a batterys electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navys quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








