Home > Press > Acoustic tweezers moves cells in three dimensions, builds structures
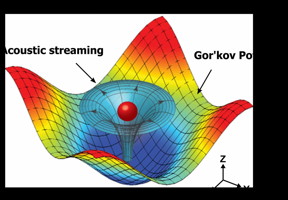 |
| Numerical simulation results mapping the acoustic field around a particle that shows the physical operating principle for the 3-D acoustic tweezers. The 3-D trapping node in the microfluidic chamber is created by two superimposed, orthogonal, standing surface acoustic waves and the induced acoustic streaming. CREDIT: Tony Jun Huang, Penn State |
Abstract:
Acoustic tweezers that can move single cells in three dimensions using surface acoustic waves without touching, deforming or labeling the cells are possible, according to a team of engineers.
Acoustic tweezers moves cells in three dimensions, builds structures
University Park, PA | Posted on January 26th, 2016"In this application we use surface acoustic waves to create nodes where cells or microparticles are trapped," said Tony Jun Huang, professor and The Huck Distinguished Chair in Bioengineering Science and Mechanics. "We can then move the cell or particle in three dimensions to create structures in two or three dimensions."
The trapping nodes are formed by two sets of surface-acoustic-wave generators. When the sound waves from opposite sides meet, they create pressure that catches and positions the particle or cell. Moving the location where the sound waves meet moves the location of the cell or particle. These standing-wave shifts manipulate the tiny objects in two dimensions. The amplitude of the acoustic vibrations controls the movement in the third dimension. The researchers report their work in today's (Jan. 25) issue of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"The results presented in this paper provide a unique pathway to manipulate biological cells, accurately and in three dimensions, without the need for any invasive contact, tagging, or biochemical labeling," said Subra Suresh, president, Carnegie Mellon University and part of the research team. "This approach could lead to new possibilities for research and applications in such areas as regenerative medicine, neuroscience, tissue engineering, biomanufacturing, and cancer metastasis."
The research team not only created a 3-D tweezers, but they also modeled bioprinting with this device and used the device to pick up, translate and print single cells and cell assemblies, creating 2-D and 3-D structures in a precise, noninvasive manner. They demonstrated this ability by capturing a single suspended mouse fibroblast and moving it to a targeted location in the microfluidic chamber.
Bioprinting to recreate biological materials must include a way to preserve cell-to-cell communications and cell-environment interactions. While the device is not a 3-D printer in the conventional sense, it can move specific cells and particles to specified places and attach them wherever they belong in a functional way.
"Adding a third dimension for precisely manipulating single cells for bioprinting further advances acoustic tweezers technology," said Ming Dao, director, Nanomechanics Lab, Massachusetts Institute of Technology. "The accompanying modeling provides solutions for cell manipulation, enabling validation of the method as well as possible system optimization."
The third dimension achieved with this device relies on acoustic streaming, a type of fluidic motion induced by a standing acoustic wave. By manipulating the acoustic wave, the researchers could position the trapped particle or cell wherever they wanted it within the vertical confines of the enclosed fluid.
"3-D acoustic tweezers can pattern cells with control over the number of cells, cell spacing and the confined geometry, which may offer a unique way to print neuron cells to create artificial neural networks for neuron science applications or regenerative neuron medicine," said Huang.
The current device can place a cell or particle with 1 micrometer accuracy horizontally and with 2 micrometer accuracy vertically. The researchers moved a 10 micrometer particle at an average speed of about 2.5 micrometers per second and could place cells in several seconds to a few minutes depending on the distance.
Because the acoustic wavelength and input power are instantaneously tunable during experiments, the placement accuracy is only limited by the resolution of the device setup, according to the researchers.
###
Also working on this project were Feng Guo, Peng Li and James Lata, postdoctoral Fellows in engineering science and mechanics; Zhangming Mao and Yuchao Chen, graduate students in engineering science and mechanics; Zhiwei Xie, former postdoctoral Fellow in biomedical engineering; and Jian Yang, professor of biomedical engineering, all at Penn State.
The National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation suported this work.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
A'ndrea Elyse Messer
814-865-9481
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








