Home > Press > The subtle dance of atoms influences enzyme activity: Certain infinitesimal fluctuations of distant atoms can control enzyme function even though they are not directly involved in enzyme catalysis
 |
Abstract:
Infinitesimal fluctuations occurring on the milli- and even nano-second time scales within the three-dimensional structure of enzymes may be one of the keys to explaining protein function. Professor Nicolas Doucet's team at INRS has demonstrated that even when certain amino acids are far from the active site of an enzyme, a change in their flexibility and atomic fluctuations can significantly impact enzyme activity. This phenomenon, which has been underestimated up to now, could explain certain protein engineering failures and help improve the way synthetic functional enzymes are designed.
The subtle dance of atoms influences enzyme activity: Certain infinitesimal fluctuations of distant atoms can control enzyme function even though they are not directly involved in enzyme catalysis
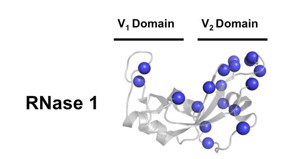
Québec, Canada | Posted on December 10th, 2015Enzymes are nanomachines that are exceptionally efficient at catalyzing a chemical reaction. They play a role in all cellular mechanisms. Like all proteins, they are made up of amino acid chains that are folded and assembled in a very precise 3D structure. Some enzymes, like ribonuclease A, are so efficient that they catalyze the transformation of chemical molecules thousands of times per second.
In this study, Donald Gagné, a researcher in Professor Doucet's lab holding a PhD in biology from INRS, analyzed the impact of removing a methyl group located near a loop distant from the reaction site of ribonuclease A--a very slight change that presumably would have no effect. The mutation does not perturb the 3D structure of the enzyme. However, it did result in a four-fold reduction in the affinity of ribonuclease A for nucleotides (molecules to which it must bind to carry out its function). How is this possible?
Using crystallography techniques and nuclear magnetic resonance to examine the enzyme at atomic resolution, Donald Gagné compared normal ribonuclease A with the mutated enzyme. He observed that when ribonuclease A is modified, the nucleotides do not position themselves correctly and have a harder time binding to the active site. It appears that this repositioning is due to an increase in enzyme fluctuations caused by the elimination of this distant methyl group, which we can picture as creating vibrations that spread through the enzyme structure all the way to the site of catalysis.
This demonstration of the importance of enzyme dynamics could change our understanding of protein and enzyme mechanisms. While it remains a challenge to measure fluctuations at this atomic scale, researchers have studied the three-dimensional structure of proteins to understand how they function. Despite the staggering complexity of this phenomenon, we now know that proteins are increasingly regulated by the subtle dance of their atoms.
####
About INRS
INRS is a graduate-level research and training university and ranks first in Canada for research intensity (average grant funding per faculty member). INRS brings together some 150 professors and close to 700 students and postdoctoral fellows in its four centres located in Montreal, Quebec City, Laval, and Varennes. Its applied and fundamental research is essential to the advancement of science in Quebec and internationally, playing a key role in the development of tangible solutions to the problems faced by our society.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Stéphanie Thibault
514-499-6612
Copyright © INRS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








