Home > Press > Tokyo Institute of Technology research: Catalyst redefines rate limitations in ammonia production
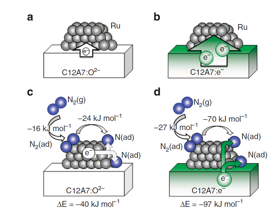 |
| Ab initio simulations of N2 interaction with the Ru/C12A7 catalysts. Character of the charge redistribution between C12A7 substrate and deposited Ru clusters is shown for the stoichiometric (a) and the electride (b) C12A7. (c,d) Adsorption energies of N2 on C12A7-supported Ru, charge transfer in the process of N2 dissociation (N2(g)+ Ru → 2N(ad) +Ru) and the corresponding energy gain (ΔE). In Ru/C12A7:O2– system (c), N2 and N accept electron charge from the Ru cluster, making it positively charged. In Ru/C12A7:e– (d), the electron charge is transferred from the substrate, leaving the Ru cluster nearly neutral. N2(g), N2(ad) and N(ad) represent N2 in gas phase, adsorbed N2, and adsorbed nitrogen atom, respectively. |
Abstract:
Studies by researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology have developed a catalyst that is so effective at promoting dissociation of the nitrogen bond in ammonia production reactions that it is no longer the step limiting the rate of the reaction.
Tokyo Institute of Technology research: Catalyst redefines rate limitations in ammonia production
Tokyo, Japan | Posted on March 30th, 2015Ammonia (NH3) is crucial for the industrial synthesis of fertilizers and pharmaceuticals so that ways to improve its production from molecular nitrogen and hydrogen are in high demand. So far the main challenge has been breaking the triple bond in nitrogen molecules, which is the strongest bond in a molecule of two atoms. Now a collaboration of researchers in Japan, the UK and the US have developed a catalyst that is so effective towards the break of the nitrogen triple bond and found that this is no longer the rate-limiting step of the reaction.
Certain oxides can be very effective at enhancing the catalytic activity of ruthenium and iron but they are unstable in ammonia synthesis conditions. Recently the electride 12CaO·7Al2O3:e- (C12A7:e-) - an ionic compound with an electron acting as the negative ion - was found to be stable at room temperature. The discovery prompted Hideo Hosono and colleagues at Tokyo Institute of Technology and the Japan Science and Technology Agency in Japan, University College London in UK and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory in US to investigate Ru/C12A7:e- as a catalyst in ammonia production.
The researchers examined the N2 isotope exchange and hydrogen adsorption/desorption reactions. They observed a remarkable level of catalytic activity at less than half the activation energy of other catalysts. In addition the catalyst did not degrade due to hydrogen poisoning as is usually the case for ruthenium-based catalysts.
Further studies and density functional calculations suggested a mechanism for the reaction. "Fast N2 cleavage is ensured by highly efficient electron transfer from C12A7:e- to N2 molecules adsorbed on the Ru nanoparticles," the researchers conclude in their report. "As a result, the bottleneck in the NH3 synthesis reaction is shifted from the N-N triple bond dissociation to the formation of nitrogen-hydrogen species."
Background
Haber-Bosch
Both iron and ruthenium are well known catalysts for the break of the nitrogen bond. However ruthenium-based catalysts are highly prone to hydrogen poisoning where hydrogen adsorbs to the catalyst, so that for over a century iron-based catalysts have remained central to the widely implemented ammonia production process developed by Fritz Haber and Carl Bosch in 1909.
Alkali and alkaline earth metal oxides enhance ruthenium and iron catalysts by donating electrons into the ‘antibonding orbitals' of the nitrogen, weakening the bond. This is referred to as the electronic promoting effect but has so far been difficult to harness for ammonia synthesis because the oxides are unstable in the reaction conditions.
Catalyst structure
The promoter the researchers investigated is a combination of oxides of calcium (an alkaline earth metal) and aluminium in the form of an electride - 12CaO·7Al2O3:e- (C12A7:e-). The same ionic compound can be used with oxides or hydrides acting as the anion instead of an electron as in the electride studied, but these are far less effective.
The crystal structure of C12A7:e- consists of a positively charged framework having the chemical formula [Ca24Al28O64]4+, and four extra framework electrons accommodated in the cages as counter ions. This structure has uniquely versatile characteristics for the exchange of negatively charged ions.
Shifting the bottleneck
The researchers monitored N2 isotope exchange and hydrogen adsorption/desorption reactions. From these observations the researchers determined that breaking the nitrogen triple bond was no longer the rate-limiting step of ammonia synthesis with the Ru/C12A7:e-. Instead they suggest that the subsequent formation of the nitrogen-hydrogen bond in ammonia is now the bottleneck in the process.
The researchers also calculated the order of the reaction from the effect on the rate as the concentrations of the chemicals were varied. The catalyst had a lower reaction order for nitrogen than other catalysts suggesting a different mechanism, and that the nitrogen populates the catalyst more densely than for other catalysts.
Catalyst stability
The Ru/C12A7:e- catalyst was not subject to hydrogen poisoning and remained active at high pressure. The researchers suggest that the fast formation of ammonia on the ruthenium surface limits hydrogen being incorporated into the catalyst so that its activity remains unchanged.
Further studies suggest that the reversible hydrogen storage-release properties are responsible for the reaction mechanism of the new catalyst. This mechanism switches at temperatures below 593 K at which temperatures the catalyst becomes prone to hydrogen poisoning like other catalysts.
Reference
Title: Electride support boosts nitrogen dissociation over ruthenium Q1 catalyst and shifts the bottleneck in ammonia synthesis.
Journal: NATURE COMMUNICATIONS, On line, 30 March 2015
Digital Object Indicator (DOI): 10.1038/ncomms7731
Authors: Masaaki Kitano1, Shinji Kanbara2, Yasunori Inoue2, Navaratnarajah Kuganathan3, Peter V. Sushko4,5,Toshiharu Yokoyama1,5, Michikazu Hara2,5 & Hideo Hosono1,2,5,6
1Materials Research Center for Element Strategy, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8503, Japan.
2Materials andStructures Laboratory, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8503, Japan.
3 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK.
4 Fundamental and Computational Sciences Directorate, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, Washington 99352, USA.
5 ACCEL, Japan Science and Technology Agency, 4-1-8 Honcho, Kawaguchi, Saitama 332-0012, Japan.
6 Frontier Research Center, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259 Nagatsuta, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8503, Japan.
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to M.H. (email: ) or to H.H. (email: ).
####
About Tokyo Institute of Technology
As one of Japan’s top universities, Tokyo Institute of Technology seeks to contribute to civilization, peace and prosperity in the world, and aims at developing global human capabilities par excellence through pioneering research and education in science and technology, including industrial and social management. To achieve this mission, we have an eye on educating highly moral students to acquire not only scientific expertise but also expertise in the liberal arts, and a balanced knowledge of the social sciences and humanities, all while researching deeply from basics to practice with academic mastery. Through these activities, we wish to contribute to global sustainability of the natural world and the support of human life.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Asuka Suzuki
Center for Public Affairs and Communications
Tokyo Institute of Technology
2-12-1, Ookayama, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 152-8550, Japan
Tel: +81-3-5734-2975
Fax: +81-3-5734-3661
Copyright © Tokyo Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








