Home > Press > Race of the electrons: Laser pulses can be used to track the motion of electrons in metals with attosecond precision. This helps to understand and possibly improve important electronic effects.
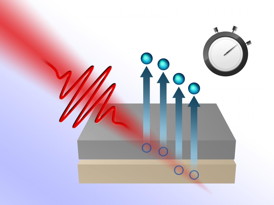 |
| In this image, a laser beam removes electrons from a layered metal structure. Attosecond technology allows scientists to measure time delays between electrons from different metal layers.
CREDIT: Vienna University of Technology |
Abstract:
It is easy to measure electric current. But it is extremely hard to watch the individual electrons which make up this current. Electrons race through the metal with a speed of several million meters per second, and the distance they have to cover between two adjacent atoms is very small. This means that tiny time intervals have to be resolved in order to watch the electrons dashing through the metal.
Race of the electrons: Laser pulses can be used to track the motion of electrons in metals with attosecond precision. This helps to understand and possibly improve important electronic effects.
Vienna, Austria | Posted on January 14th, 2015Measurements in Garching (Germany) and theoretical calculations at the Vienna University of Technology (Austria) have now made this possible. As it turns out, the motion of the electrons in the metal is remarkably similar to ballistic motion in free space. The results have now been published in the journal "Nature".
The Tiny Timescales of the Quantum World
Albert Einstein already explained the "photoelectric effect" in 1905: light transfers energy to an electron, removing it from the metal. This happens so fast that for a long time it seemed impossible to study the time evolution of this process. In recent years, however, attosecond physics has advanced dramatically, so that time resolved analysis of this process has become possible.
An attosecond is a billionth of a billionth of a second (10^-18 seconds). This is approximately the time it takes light to travel the distance from one atom to the next. Using ultrashort laser pulses, time can now be measured with a precision in the attosecond range.
The data which has now been published in "Nature" was measured at the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics in Garching, in a collaboration with TU Munich, the Fritz Haber Institute in Berlin, the Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter in Hamburg and LMU Munich. At the Vienna University of Technology, theoretical models and large-scale computer simulations have been developed, in order to analyse and interpret the results.
Racing Electrons
"The experiment allows us to watch a race of electrons", says Professor Joachim Burgdörfer (TU Vienna). Two different metals - tungsten and magnesium - are stacked and hit with a laser pulse. Either in the magnesium or in the tungsten layer, the light can remove electrons, which then find their way to the surface. The distance the electrons have to cover is less than a nanometer, but still it is possible to quantify the lead of the electrons from the magnesium layer, arriving shortly before the electrons from the tungsten layer.
The distance of this race can be tuned: one to five atomic layers of magnesium are deposited on tungsten. "The thicker the magnesium layer, the larger the lead of its electrons compared to the electrons coming from the tungsten layer", says Christoph Lemell (TU Vienna). The simple relationship between layer thickness and arrival time shows that the electrons travel through the metal ballistically, on rather undisturbed and straight lines. Complex scattering processes do not play an important role on theses time and length scales.
For precise timing, it is crucial to have a very well defined finish line. For the photo-finish, a second laser was used. It influences the electrons the moment they left the metal, but not before. The laser beam must not penetrate the metal. "Within a distance shorter than the spacing between the metal atoms, the intensity of the laser field changes dramatically", says Georg Wachter (TU Vienna). The field of the laser beam is reduced to almost zero in the outermost layer, whereas right outside the metal the electrons immediately enter a strong laser field. This sharp contrast is the reason these extremely precise time measurements become possible.
The new findings are expected to help with the miniaturization of electronic and photonic elements - and they are another proof for the amazing possibilities of attosecond physics. "This new area of research gives us new methods to develop quantum technologies and study fundamental questions of materials science and electronics", says Joachim Burgdörfer.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Florian Aigner
0043-158-801-41027
Prof. Christoph Lemell
Institute for Theoretical Physics
Vienna University of Technology
T: +43-1-58801-13612
Dr. Georg Wachter
Institute for Theoretical Physics
Vienna University of Technology
T: +43-1-58801-13630
Prof. Joachim Burgdörfer
Institute for Theoretical Physics
Vienna University of Technologyn
Copyright © Vienna University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








