Home > Press > New NIST metamaterial gives light a one-way ticket
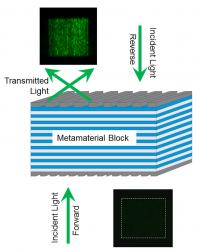 |
| This is a schematic of NIST's one-way metamaterial. Forward traveling green light (left) or red light passes through the multilayered block and comes out at an angle due to diffraction off of grates on the surface of the material. Light traveling in the opposite direction (right) is almost completely filtered by the metamaterial and can't pass through.
Credit: Xu/NIST |
Abstract:
The light-warping structures known as metamaterials have a new trick in their ever-expanding repertoire. Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have built a silver, glass and chromium nanostructure that can all but stop visible light cold in one direction while giving it a pass in the other.* The device could someday play a role in optical information processing and in novel biosensing devices.
New NIST metamaterial gives light a one-way ticket
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on July 2nd, 2014In recent years, scientists have designed nanostructured materials that allow microwave or infrared light to propagate in only one direction. Such structures hold potential for applications in optical communication—for instance, they could be integrated into photonic chips that split or combine signals carried by light waves. But, until now, no one had achieved one-way transmission of visible light, because existing devices could not be fabricated at scales small enough to manipulate visible light's short wavelengths. (So-called "one-way mirrors" don't really do this—they play tricks with relative light levels.)
To get around that roadblock, NIST researchers Ting Xu and Henri Lezec combined two light-manipulating nanostructures: a multi-layered block of alternating silver and glass sheets and metal grates with very narrow spacings.
The silver-glass structure is an example of a "hyperbolic" metamaterial, which treats light differently depending on which direction the waves are traveling. Because the structure's layers are only tens of nanometers thick—much thinner than visible light's 400 to 700 nanometer wavelengths—the block is opaque to visible light coming in from outside. Light can, however, propagate inside the material within a narrow range of angles.
Xu and Lezec used thin-film deposition techniques at the NIST NanoFab user facility to build a hyperbolic metamaterial block.Guided by computer simulations, they fabricated the block out of 20 extremely thin alternating layers of silicon dioxide glass and silver. To coax external light into the layered material, the researchers added to the block a set of chromium grates with narrow, sub-wavelength spacings chosen to bend incoming red or green light waves just enough to propagate inside the block. On the other side of the block, the researchers added another set of grates to kick light back out of the structure, although angled away from its original direction.
While the second set of grates let light escape the material, their spacing was slightly different from that of the first grates. As a result, the reverse-direction grates bent incoming light either too much or not enough to propagate inside the silver-glass layers. Testing their structures, the researchers found that around 30 times more light passed through in the forward direction than in reverse, a contrast larger than any other achieved thus far with visible light.
Combining materials that could be made using existing methods was the key to achieving one-way transmission of visible light, Lezec says. Without the intervening silver-and-glass blocks, the grates would have needed to be fabricated and aligned more precisely than is possible with current techniques. "This three-step process actually relaxes the fabrication constraints," Lezec says.
In the future, the new structure could be integrated into photonic chips that process information with light instead of electricity. Lezec thinks the device also could be used to detect tiny particles for biosensing applications. Like the chrome grates, nanoscale particles also can deflect light to angles steep enough to travel through the hyperbolic material and come out the other side, where the light would be collected by a detector. Xu has run simulations suggesting such a scheme could provide high-contrast particle detection and is hoping to test the idea soon. "I think it's a cool device where you would be able to sense the presence of a very small particle on the surface through a dramatic change in light transmission," says Lezec.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mark Esser
301-975-8735
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








