Home > Press > Illinois researchers combine weak chemical forces to strengthen a novel imaging technology
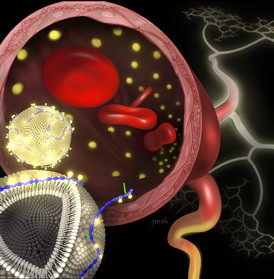 |
| Image created by Janet Sinn-Hanlon, DesignGroup@VetMed, University of Illinois |
Abstract:
When Associate Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Hyunjoon Kong, graduate student Cartney Smith, and colleagues set out to improve MR imaging (MRI), they turned current contrast agent technology on its head—or rather, they turned it inside out. The new compound they designed in collaboration with Roger Adams Professor of Chemistry Steven C. Zimmerman is not only more effective, but also self-assembling. Kong is a member of the Regenerative Biology and Tissue Engineering research theme at the Institute for Genomic Biology.
Illinois researchers combine weak chemical forces to strengthen a novel imaging technology
Urbana, IL | Posted on May 21st, 2014When doctors perform an MRI, they administer a contrast agent: a chemical that, when injected into the bloodstream or ingested by the patient just before the MRI, improves the clarity of structures or organs in the resulting image. One common class of contrast agent, often used for imaging of blood vessels and internal bleeding, contains gadolinium, a rare-earth metal.
Recently, biomedical researchers have found ways to increase the effectiveness of certain contrast agents by associating them with nanoparticles. The contrast agent being used is packaged inside or bonded to the surface of microscopic particles, which can be designed to target certain regions of the body or prolong the agent's activity.
Researchers are now exploring the multipurpose use of nanoparticles. If particles could be loaded with several types of contrast agents or dyes instead of one, or a contrast agent along with another type of diagnostic aid or a medication, doctors could more efficiently test for and treat conditions, and limit the number of injections received by patients.
Just like toddlers sharing a new toy, though, compounds packaged together into a nanoparticle cannot always play well together. For example, contrast agents may bind to other chemicals, reducing their effectiveness. In addition, when contrast agents are enclosed inside a nanoparticle, they may not work as well. Attempts to attach agents to the outer surface of nanoparticles via covalent formation are also problematic, as they can negatively affect the activity of the nanoparticles or the compounds that they carry.
Kong, Smith and colleagues tackled these challenges by using interactions between naturally occurring biomolecules as a guide. Many types of proteins are strongly attached to cell membranes not by covalent bonds, but by the sum of multiple weaker forces—the attraction of positive and negative charges, and the tendency of non-polar (oil-like) substances to seek each other and avoid water.
The group hypothesized that the same types of forces could be used to attach a contrast agent to the surface of a type of nanoparticle called a liposome, which resembles a little piece of cell membrane in the shape of a tiny bubble. The researchers designed a "fastener" molecule, DTPA-chitosan-g-C18, that is charged, attracting it to the liposome and binding it to the contrast agent gadolinium. A nonpolar region anchors it to the liposome membrane.
In a series of experiments reported in a recent ACS Nano article (DOI: 10.1021/nn4026228), Kong and others demonstrated that their fastener molecule readily inserted itself into the membrane of pre-made liposomes. Gadolinium stably associated with the modified nanoparticles in solution, and experiments in animal models showed that these nanoparticles produced clear diagnostic images.
"The strategy works like Velcro on a molecular level to adhere functional units to the outer leaflet of a liposome," said Smith, who was first author on the study. "This work represents a new material design strategy that is scalable and easily implemented. The development of improved contrast agents has the potential to directly impact patients' lives by detecting damaged blood vessels."
One of the difficulties of working with liposomes is their tendency to degrade inside the body. When the fastener-loaded liposomes degraded, some of the efficacy of the gadolinium was lost. In a second study published in Langmuir (DOI: 10.1021/la500412r), Kong and Smith developed a process for chemically cross-linking the components of the nanoparticle that prolonged the life of the nanoparticles in biological conditions.
The work reported in ACS Nano was a collaboration among Kong, Smith, Zimmerman, and others at the University of Illinois, as well as Dr. Sanjay Misra and researchers at the Mayo Clinic. Both studies were supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health, as well as the University of Illinois Center for Advanced Study.
Written By:
Claudia Lutz. Photos by L. Brian Stauffer and Janet Sinn-Hanlon.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Nicholas Vasi
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








