Home > Press > Improved Supercapacitors for Super Batteries, Electric Vehicles: Researchers develop novel supercapacitor architecture that provides two times more energy and power compared to supercapacitors commercially available today
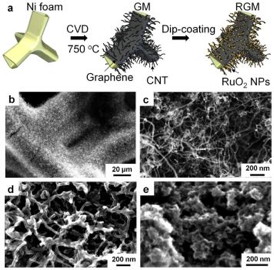 |
| (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation process of RGM nanostructure foam. SEM images of (b–c) as-grown GM foam (d) Lightly loaded RGM, and (e) heavily loaded RGM. |
Abstract:
Researchers at the University of California, Riverside have developed a novel nanometer scale ruthenium oxide anchored nanocarbon graphene foam architecture that improves the performance of supercapacitors, a development that could mean faster acceleration in electric vehicles and longer battery life in portable electronics.
Improved Supercapacitors for Super Batteries, Electric Vehicles: Researchers develop novel supercapacitor architecture that provides two times more energy and power compared to supercapacitors commercially available today
Riverside, CA | Posted on May 19th, 2014The researchers found that supercapacitors, an energy storage device like batteries and fuel cells, based on transition metal oxide modified nanocarbon graphene foam electrode could work safely in aqueous electrolyte and deliver two times more energy and power compared to supercapacitors commercially available today.
The foam electrode was successfully cycled over 8,000 times with no fading in performance. The findings were outlined in a recently published paper, "Hydrous Ruthenium Oxide Nanoparticles Anchored to Graphene and Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Foam for Supercapacitors," in the journal Nature Scientific Reports.
The paper was written by graduate student Wei Wang; Cengiz S. Ozkan, a mechanical engineering professor at UC Riverside's Bourns College of Engineering; Mihrimah Ozkan, an electrical engineering professor; Francisco Zaera, a chemistry professor; Ilkeun Lee, a researcher in Zaera's lab; and other graduate students Shirui Guo, Kazi Ahmed and Zachary Favors.
Supercapacitors (also known as ultracapacitors) have garnered substantial attention in recent years because of their ultra-high charge and discharge rate, excellent stability, long cycle life and very high power density.
These characteristics are desirable for many applications including electric vehicles and portable electronics. However, supercapacitors may only serve as standalone power sources in systems that require power delivery for less than 10 seconds because of their relatively low specific energy.
A team led by Cengiz S. Ozkan and Mihri Ozkan at UC Riverside are working to develop and commercialize nanostructured materials for high energy density supercapacitors.
High capacitance, or the ability to store an electrical charge, is critical to achieve higher energy density. Meanwhile, to achieve a higher power density it is critical to have a large electrochemically accessible surface area, high electrical conductivity, short ion diffusion pathways and excellent interfacial integrity. Nanostructured active materials provide a mean to these ends.
"Besides high energy and power density, the designed graphene foam electrode system also demonstrates a facile and scalable binder-free technique for preparing high energy supercapacitor electrodes," Wang said. "These promising properties mean that this design could be ideal for future energy storage applications."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sean Nealon
951-827-1287
Twitter: seannealon
Additional Contacts
Cengiz Ozkan
Tel: 951-827-5016
Copyright © University of California - Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








