Home > Press > Ames Lab researchers see rare-earth-like magnetic properties in iron
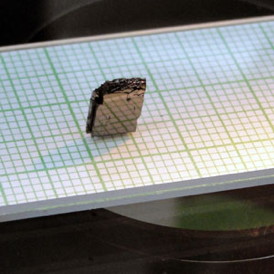 |
| A single crystal of lithium-iron nitride. Scientists at Ames Laboratory observed magnetic properties in iron-ions in these lithium-iron nitrides that are typically associated withrare-earth elements. |
Abstract:
Scientists at the Department of Energy's Ames Laboratory have observed magnetic properties typically associated with those observed in rare-earth elements in iron. These properties are observed in a new iron based compound that does not contain rare earth elements, when the iron atom is positioned between two nitrogen atoms. The discovery opens the possibility of using iron to provide both the magnetism and permanence in high-strength permanent magnets, like those used in direct-drive wind turbines or electric motors in hybrid cars. The results appeared in Nature Communications.
Ames Lab researchers see rare-earth-like magnetic properties in iron
Ames, IA | Posted on April 28th, 2014In modern magnets, iron gives most magnets their strength, and comes with the benefits of being abundant and cheap. But the magnet recipe must also include rare earth elements, which lend magnets "permanence," or the ability to keep the direction of the magnetic field fixed (also called anisotropy). The challenge is rare-earths materials are expensive and at risk of domestic supply shortages. So, ideal next-generation permanent magnets will rely more heavily on iron or other abundant materials and less on rare earths.
"The breakthrough here is that we see magnetic anisotropy normally associated with rare earths ions in iron," said Paul Canfield, Ames Laboratory physicist. "This isn't an industrial breakthrough at this point because these magnetic properties only reveal themselves at cryogenic temperatures. But, it's a basic science breakthrough that hopefully will point the way to future technical breakthroughs."
Image
A single crystal of lithium-iron nitride. Scientists
at Ames Laboratory observed magnetic
properties in iron-ions in these lithium-iron
nitrides that are typically associated with
rare-earth elements.
Canfield's research group is internationally known for expertise in design, discovery, growth and characterization of new and promising materials. In this effort, Canfield and his colleagues, including postdoctoral research associate Anton Jesche, designed a new technique to grow lithium-iron-nitride single crystals from a lithium-nitrogen solution.
"Using nitrogen in solution growth had not yet been well explored because, since we typically think of nitrogen as a gas, it's challenging to get into a solution" said Jesche, "But we found that lithium - lightest solid element -- looked like it could hold nitrogen in solution. So, we mixed together lithium and lithium-nitride powder, and it worked. It created a solution."
Then the group added in iron and, to their surprise, the iron dissolved.
"Usually iron and lithium don't mix," said Canfield, who is also a Distinguished Professor of physics and astronomy at Iowa State University. "It seems adding nitrogen to the lithium in the solution allows iron to go in."
The resulting single crystals of iron-substituted lithium nitride yielded even more surprises: the opposing external field required to reverse magnetization was more than 11 tesla, as much as an order of magnitude larger than that of commercially available permanent magnets and two or more orders of magnitude larger than is typically found in single crystals. Further evidence of iron's exotic state in this compound is the field-induced quantum tunneling found for very diluted iron concentrations at the relatively high temperature of 10 Kelvin, a temperature orders of magnitude higher than what had been seen before.
"With detailed measurements, we saw that these single iron ions are indeed behaving like a single rare-earth ion would," Canfield continued. "And we believe this has to do with the special, fairly simple, geometry that the iron finds itself in: one iron atom positioned between two nitrogen atoms. We hope this crystal growing technique and this specific material can be a model system for further theoretical study of these rare-earth-like iron ions. As it stands, these materials have clear implications on finding rare-earth-free replacements for permanent magnets -- and perhaps also may impact data storage and manipulation in quantum computer applications."
The research is funded by the DOE's Office of Science.
The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit the Office of Science website at science.energy.gov/.
####
About DOE/Ames Laboratory
Ames Laboratory is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory operated by Iowa State University for DOE’s Office of Science. Ames Laboratory creates innovative materials, technologies and energy solutions. We use our expertise, unique capabilities and interdisciplinary collaborations to solve global problems.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Breehan Gerleman Lucchesi
515-294-9750
Paul Canfield
Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering
515-294-6270
Copyright © DOE/Ames Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








