Home > Press > Silver Nanowire Sensors Hold Promise for Prosthetics, Robotics
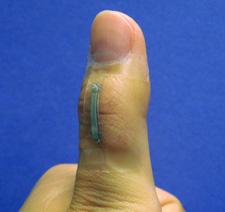 |
| A sensor based on silver nanowires is mounted onto a thumb joint to monitor the skin strain associated with thumb flexing. The sensor shows good wearability and large-strain sensing capability. Photo: Shanshan Yao. |
Abstract:
"Wearable Multifunctional Sensors Using Printed Stretchable Conductors Made Of Silver Nanowires"
Authors: Shanshan Yao and Yong Zhu, North Carolina State University
Published: Online Jan. 14, Nanoscale
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR05496A
Abstract: Considerable efforts have been made to achieve highly sensitive and wearable sensors that can simultaneously detect multiple stimuli such as stretch, pressure, temperature or touch. Here we develop highly stretchable multifunctional sensors that can detect strain (up to 50%), pressure (up to ~1.2 MPa) and finger touch with high sensitivity, fast response time (~40 ms) and good pressure mapping function. The reported sensors utilize the capacitive sensing mechanism, where silver nanowires are used as electrodes (conductors) and Ecoflex is used as a dielectric. The silver nanowire electrodes are screen printed. Our sensors are demonstrated for several wearable applications including monitoring thumb movement, sensing the strain of knee joint in patellar reflex (knee-jerk) and other human motions, illustrating the potential utilities of such sensors in robotic systems, prosthetics, healthcare and flexible touch panels.
Silver Nanowire Sensors Hold Promise for Prosthetics, Robotics
Raleigh, NC | Posted on January 16th, 2014North Carolina State University researchers have used silver nanowires to develop wearable, multifunctional sensors that could be used in biomedical, military or athletic applications, including new prosthetics, robotic systems and flexible touch panels. The sensors can measure strain, pressure, human touch and bioelectronic signals such as electrocardiograms.
"The technology is based on either physical deformation or "fringing" electric field changes. The latter is very similar to the mechanism used in smartphone touch screens, but the sensors we've developed are stretchable and can be mounted on a variety of curvilinear surfaces such as human skin," says Shanshan Yao, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of a paper on the work.
"These sensors could be used to help develop prosthetics that respond to a user's movement and provide feedback when in use," says Dr. Yong Zhu, an associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NC State and senior author of the paper. "They could also be used to create robotics that can ‘feel' their environment, or the sensors could be incorporated into clothing to track motion or monitor an individual's physical health."
The researchers built on Zhu's earlier work to create highly conductive and elastic conductors made from silver nanowires. Specifically, the researchers sandwiched an insulating material between two of the stretchable conductors. The two layers then have the ability - called "capacitance" - to store electric charges. Pushing, pulling or touching the stretchable conductors changes the capacitance. The sensors work by measuring that change in capacitance.
"Creating these sensors is simple and low cost," Yao says. "And we've already demonstrated the sensors in several prototype applications."
For example, the researchers employed these sensors to monitor thumb movement, which can be useful in controlling robotic or prosthetic devices. The researchers also demonstrated an application to monitor knee movements while a test subject is running, walking and jumping.
"The deformation involved in these movements is large, and would break a lot of other sensor devices," Zhu says. "But our sensors can be stretched to 150 percent or more of their original length without losing functionality, so they can handle it."
The researchers also developed an array of sensors that can map pressure distribution, which is important for use in robotics and prosthetics applications. The sensors exhibit a quick response time - 40 milliseconds - so strain and pressure can be monitored in real time.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Dr. Yong Zhu
919.513.7735
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
Light guide plate based on perovskite nanocomposites November 3rd, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Flexible Electronics
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








