Home > Press > Great potential for faster diagnoses with new method
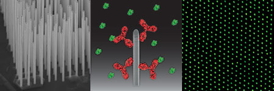 |
| Left: Electron microscope image of nanowire forest. Middle: Diagram of a single nanowire with proteins (red molecules) which captures a different type proteins (green molecules) from a solution. Right: Typical fluorescence microscope image of proteins captures on nanowires (seen from above). |
Abstract:
The more accurately we can diagnose a disease, the greater the chance that the patient will survive. That is why many researchers are working to improve the quality of the diagnostic process. Researchers at the Nano-Science Center, University of Copenhagen have discovered a method that will make the process faster, cheaper and more accurate. This is possible, because they are combining advanced tools used in physics for research in biology at nanoscale, two scientific disciplines usually very distant from each other.
Great potential for faster diagnoses with new method
Copenhagen, Denmark | Posted on October 3rd, 2013Many diseases can be diagnosed using so-called biomarkers. There are substances, for example, that can be measured in a blood sample, which shows that the patient is suffering from the disease in question. These biomarkers are often proteins that are found in very small quantities in the blood, making it difficult to detect them. By measuring them, the diagnosing is more precise and many diseases can be detected very early, before the patient develops severe symptoms.
We have developed a method in which we optimise the analysis of the proteins. A central point of this method is the use of nanowires to hold the proteins while we analyse them. It is unique, explains Katrine R. Rostgaard, a PhD student at the Nano-Science Center, Department of Chemistry, University of Copenhagen.
Researchers normally use small plates to hold the proteins when they need to be analysed, but by using nanowires, which are cylindrical structures having a diameter of about 1/1000th of a human hair, they add a third dimension to the sample. The nanowires stand up like a little forest, creating a much greater surface area to hold the proteins because they can sit on all sides of the nanowire.
- With greater area, we can hold more proteins at once. This makes it possible to measure for multiple biomarkers simultaneously and it increases the signal, thereby providing a better quality of diagnosis, says Katrine R. Rostgaard about the method, which has just been published in the journal Nanoscale.
Profitable method for diagnosing
The research is done at the nanoscale on small size samples. The forests of nanowires are used to capture the proteins they want to study directly. When examining the proteins, you can reuse the nanowires by performing a multiple tests on the same protein. This simplifies the workflow in the laboratory tremendously in comparison to the conventional method, where researchers have to start over with a new plate to hold the proteins every time they perform a new analysis. In this way, the method helps to make the diagnostic process more environmentally friendly and economically viable for use in, for example, industry.
- We know that several major biotech companies will be interested in our new method and find potential applications, though it requires improvements before it is ready for use in the industry, explains Karen Martinez, research group leader of the Nanobio group at the Nano-Science Center, Department of Chemistry, University of Copenhagen.
The work is part of two larger projects, ANaCell and UNIK Center for Synthetic Biology, which is financed by The Danish Council for Strategic Research and the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karen Martinez
(45) 30-30-04-75
Copyright © University of Copenhagen
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








