Home > Press > Airbrushing Could Facilitate Large-Scale Manufacture of Carbon Nanofibers
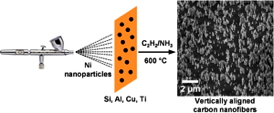 |
| This image illustrates how researchers use an airbrush to grow vertically aligned carbon nanofibers. Click to enlarge. Image: Joseph Tracy |
Abstract:
"Airbrushed Nickel Nanoparticles for Large-Area Growth of Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanofibers on Metal (Al, Cu, Ti) Surfaces"
Authors: Mehmet F. Sarac, Bryan D. Anderson, Ryan C. Pearce, Justin G. Railsback, Adedapo A. Oni, Ryan M. White, James M. LeBeau, Anatoli V. Melechko, and Joseph B. Tracy, North Carolina State University; Dale K. Hensley, Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Published: online Sept. 9, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI: 10.1021/am401889t
Abstract: Vertically aligned carbon nanofibers (VACNFs) were grown by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) using Ni nanoparticle (NP) catalysts that were deposited by airbrushing onto Si, Al, Cu, and Ti substrates. Airbrushing is a simple method for depositing catalyst NPs over large areas that is compatible with roll-to-roll processing. The distribution and morphology of VACNFs are affected by the airbrushing parameters and the composition of the metal foil. Highly concentrated Ni NPs in heptane give more uniform distributions than pentane and hexanes, resulting in more uniform coverage of VACNFs. For VACNF growth on metal foils, Si micropowder was added as a precursor for Si-enriched coatings formed in situ on the VACNFs that impart mechanical rigidity. Interactions between the catalyst NPs and the metal substrates impart control over the VACNF morphology. Growth of carbon nanostructures on Cu is particularly noteworthy because the miscibility of Ni with Cu poses challenges for VACNF growth, and carbon nanostructures anchored to Cu substrates are desired as anode materials for Li-ion batteries and for thermal interface materials.
Airbrushing Could Facilitate Large-Scale Manufacture of Carbon Nanofibers
Raleigh, NC | Posted on September 11th, 2013Researchers from North Carolina State University used airbrushing techniques to grow vertically aligned carbon nanofibers on several different metal substrates, opening the door for incorporating these nanofibers into gene delivery devices, sensors, batteries and other technologies.
"Because we're using an airbrush, this technique could easily be incorporated into large-scale, high-throughput manufacturing processes," says Dr. Anatoli Melechko, an adjunct associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and co-author of a paper describing the work. "In principle, you could cover an entire building with it."
"It's common to use nickel nanoparticles as catalysts to grow carbon nanofibers, and we were able to coat metal substrates with nickel nanoparticles using an airbrush," says Dr. Joseph Tracy, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and senior author of the paper. "Airbrushing gives us a fairly uniform coating of the substrate and it can be applied to a large area at room temperature in a short period of time."
After applying the nickel nanoparticles, the researchers airbrushed the substrate with a layer of silicon powder and heated the coated substrate to 600 degrees Celsius in a reactor filled with acetylene and ammonia gas. In the reactor, carbon nanofibers formed under the nickel nanoparticles and were held upright by a silicon-enriched coating. The finished product resembles a forest of nanofibers running perpendicular to the substrate. The researchers tested this technique successfully on aluminum, copper and titanium substrates.
"Growing carbon nanofibers on a metal substrate means the interface between the two materials is highly conductive, which makes the product more useful as an electrode material for use in a range of potential applications," says Mehmet Sarac, a Ph.D. student at NC State and lead author of the paper.
The paper, "Airbrushed Nickel Nanoparticles for Large-Area Growth of Vertically Aligned Carbon Nanofibers on Metal (Al, Cu, Ti) Surfaces," was published online Sept. 9 in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. The paper was co-authored by NC State Ph.D. students Bryan Anderson, and Adedapo Oni; former NC State graduate students Dr. Ryan Pearce and Justin Railsback; former NC State postdoctoral researcher Dr. Ryan White; Dr. James LeBeau, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State; and Dale Hensley of Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation, the Defense Threat Reduction Agency, the U.S. Department of Energy and the Republic of Turkey's Ministry of National Education.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Matt Shipman
919-515-6386
Copyright © North Carolina State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








