Home > Press > Plasma-treated nano filters help purify world water supply
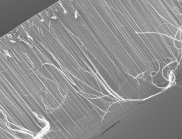 |
| Cross-sectional image of the carbon nanotubes. |
Abstract:
Access to safe drinking water is a step closer to being a reality for those in developing countries, thanks to new research published today in Nature Communications.
Plasma-treated nano filters help purify world water supply
Clayton, Australia | Posted on August 21st, 2013The study paves the way for the next generation of portable water purification devices, which could provide relief to the 780 million people around the world who face every day without access to a clean water supply.
An international team of researchers - led by Associate Professor Hui Ying Yang from Singapore University of Technology and Design - showed that water purification membranes enhanced by plasma-treated carbon nanotubes are ideal for removing contaminants and brine from water.
The team included Dr Zhaojun Han and Professor Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov from CSIRO's world-leading Plasma Nanoscience Laboratories.
According to Dr Han, these membranes could be integrated into portable water purification devices the size of a tea pot that would be rechargeable, inexpensive and more effective than many existing filtration methods. Contaminated water would go in one end, and clean drinkable water would come out the other.
"Small portable purification devices are increasingly recognised as the best way to meet the needs of clean water and sanitation in developing countries and in remote locations, minimising the risk of many serious diseases," Dr Han says.
"The large industrialised purification plants we see in other parts of the world are just not practical - they consume a large amount of energy and have high labour costs, making them very expensive to run."
Dr Han acknowledges that some smaller portable devices do already exist. However, because they rely on reverse osmosis and thermal processes, they are able to remove salt ions but are unable to filter out organic contaminants from the briny water found in some river and lake systems.
"For people in remote locations, briny water can sometimes be the only available water source," he says. "That's why it's important to not only be able to remove salts from water, but to also be able to put it through a process of purification."
"Our study showed that carbon nanotube membranes were able to filter out ions of vastly different sizes - meaning they were able to remove salt, along with other impurities," he says.
According to Professor Ostrikov, the other downside of existing portable devices is that they require a continuous power supply to operate their thermal processes. "On the other hand, the new membranes could be operated as a rechargeable device."
Professor Ostrikov attributes the success of the new membranes to the unique properties of plasma treated carbon nanotubes.
"Firstly, ultralong nanotubes have a very large surface area that is ideal for filtration. Secondly, nanotubes are easy to modify, which allows us to tailor their surface properties through localised nanoscale plasma treatment," he says.
Now that the researchers have proven the effectiveness of the method, they plan to extend their research to investigate the filtration properties of other nanomaterials. They will begin by looking at graphene, which has similar properties to carbon nanotubes, but could be made considerably denser and stronger.
The study 'Carbon nanotube membranes with ultrahigh specific capacity for water desalination and purification' is a collaborative work between Singapore University of Technology and Design, CSIRO, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the University of Sydney, and Hong Kong Polytechnic University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Crystal Ladiges
61-395-452-982
Copyright © CSIRO Australia
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Water
![]() Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Taking salt out of the water equation October 7th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








