Home > Press > Paper-thin e-skin responds to touch, holds promise for sensory robotics and interactive environments
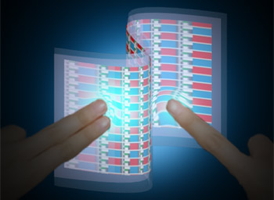 |
| In this artistic illustration of an interactive e-skin device, the intensity of the emitted light corresponds to how hard the surface is pressed. Illustration by Ali Javey and Chuan Wang |
Abstract:
A new milestone by engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, can help robots become more touchy-feely, literally.
This video shows the interactive e-skin in action. (Video by Ali Javey and Chuan Wang)
Paper-thin e-skin responds to touch, holds promise for sensory robotics and interactive environments
Berkeley, CA | Posted on July 21st, 2013A research team led by Ali Javey, UC Berkeley associate professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences, has created the first user-interactive sensor network on flexible plastic. The new electronic skin, or e-skin, responds to touch by instantly lighting up. The more intense the pressure, the brighter the light it emits.
"We are not just making devices; we are building systems," said Javey, who also has an appointment as a faculty scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. "With the interactive e-skin, we have demonstrated an elegant system on plastic that can be wrapped around different objects to enable a new form of human-machine interfacing."
This latest e-skin, described in a paper to be published online this Sunday, July 21, in the journal Nature Materials, builds on Javey's earlier work using semiconductor nanowire transistors layered on top of thin rubber sheets.
In addition to giving robots a finer sense of touch, the engineers believe the new e-skin technology could also be used to create things like wallpapers that double as touchscreen displays and dashboard laminates that allow drivers to adjust electronic controls with the wave of a hand.
"I could also imagine an e-skin bandage applied to an arm as a health monitor that continuously checks blood pressure and pulse rates," said study co-lead author Chuan Wang, who conducted the work as a post-doctoral researcher in Javey's lab at UC Berkeley.
The experimental samples of the latest e-skin measure 16-by-16 pixels. Within each pixel sits a transistor, an organic LED and a pressure sensor.
"Integrating sensors into a network is not new, but converting the data obtained into something interactive is the breakthrough," said Wang, who is now an assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering at Michigan State University. "And unlike the stiff touchscreens on iPhones, computer monitors and ATMs, the e-skin is flexible and can be easily laminated on any surface."
To create the pliable e-skin, the engineers cured a thin layer of polymer on top of a silicon wafer. Once the plastic hardened, they could run the material through fabrication tools already in use in the semiconductor industry to layer on the electronic components. After the electronics were stacked, they simply peeled off the plastic from the silicon base, leaving a freestanding film with a sensor network embedded in it.
"The electronic components are all vertically integrated, which is a fairly sophisticated system to put onto a relatively cheap piece of plastic," said Javey. "What makes this technology potentially easy to commercialize is that the process meshes well with existing semiconductor machinery."
Javey's lab is now in the process of engineering the e-skin sensors to respond to temperature and light as well as pressure.
UC Berkeley co-authors on this study are David Hwang, Zhibin Yu and Kuniharu Takei, all of whom have joint appointments at the Berkeley Lab. Additional study co-authors are Junwoo Park, Teresa Chen and Biwu Ma from the Berkeley Lab.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency and the Department of Energy helped support this research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah Yang
Media Relations
(510) 643-7741
Ali Javey
(510) 643-7263
Chuan Wang
(517) 432-4309
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Engineers make artificial skin out of nanowires (UC Berkeley press release)
Engineers make artificial skin out of nanowires (UC Berkeley press release)
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








