Home > Press > Shape-shifting nanoparticles flip from sphere to net in response to tumor signal
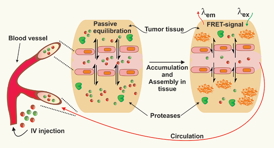 |
| Spherical nanoparticles labeled with red or green dye shift their shapes and accumulatte into netlike structures when they encounter a protease secreted by some kinds of cancerous tumors. |
Abstract:
Scientists at the University of California, San Diego, have designed tiny spherical particles to float easily through the bloodstream after injection, then assemble into a durable scaffold within diseased tissue. An enzyme produced by a specific type of tumor can trigger the transformation of the spheres into netlike structures that accumulate at the site of a cancer, the team reports in the journal Advanced Materials this week.
Shape-shifting nanoparticles flip from sphere to net in response to tumor signal
San Diego, CA | Posted on May 28th, 2013Targeting treatments specifically to cancerous or other diseased cells depends on some means of accumulating high levels of a drug or other therapeutic agent at the specific site and keeping it there. Most efforts so far depend on matching a piece of the drug-delivering molecule to specific receptors on the surface of the target cell.
Inspiration for this new strategy came from biological systems that use shape to alter the ability of something to lock in place or slip away and escape, said Nathan Gianneschi, a professor of chemistry and biochemistry, who led the project.
"We wanted to come up with a new approach," Gianneschi said. "Specifically, we wanted to design switchable materials that we could inject in one shape and have them change to another between the blood and tumors."
Some cancerous tissues produce high levels of a class of molecules called MMPs, for matrix metalloproteinases. These enzymes change how other proteins behave by altering their molecular configuration, leading to metastasis. Gianneschi and colleagues harnessed this ability to alter their nanoparticles in ways that would cause them to linger at the site of the tumor.
"We figured out how to make an autonomous material that could sense its environment and change accordingly," Gianneschi said.
Each nanoparticle is made of many detergent-like molecules with one end that mixes readily with water and another that repels it. In solution, they self assemble into balls with the water-repellant ends inside, and in that configuration can easily be injected into a vein.
When mixed with MMPs in vials, the enzymes nicked the peptides on the surface of the spheres, which reassembled into netlike threads.
The team tested the concept further by injecting their new nanoparticles into mice with human fibrosarcomas, a kind of cancer that produces high levels of MMPs.
To mark when the spheres broke down to form other structures, the chemists placed one of two fluorecent dyes, rhodamine or fluorescein, inside the spheres. In close proximity, the dyes interact to create a specific light signal called FRET for Förster Resonance Energy Transfer, when energy jumps from rhodamine to fluorescein.
Within a day they detected FRET signals indicating that the spheres had reassembled at the sites of the tumors, and the signal persisted for at least a week.
The treatment is not inherently toxic. It did not appear to change the tumors in any way, and liver and kidney, the organs most vulnerable to collateral damage from treatments because they clear toxins from the body, were normal and healthy eight days after injection.
Different versions of these nanoparticles could be designed to respond to signals inherent to other types of cancers and inflamed tissue, the authors say. The spheres can also be engineered to carry drugs, or different diagnostic probes.
Right now, this same team is developing nanoparticles that carry an infrared dye, which would enable them to visualize tumors deeper inside the body along with other materials that can be imaged with instruments commonly available in the clinic.
Co-authors include Miao-Ping Chen and Matthew Thompson in Gianneschi's group, and Christopher Barbak and David Hall in UC San Diego School of Medicine's Department of Radiology. Funding agencies include National Institutes of Health, Army Research Office and Air Force Office of Scientific Research. Gianneschi was also supported by a New Faculty Award from the Henry and Camille Dreyfus Foundation and a Research Fellowship from the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Susan Brown
858-246-0161
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








