Home > Press > Innovation could bring flexible solar cells, transistors, displays
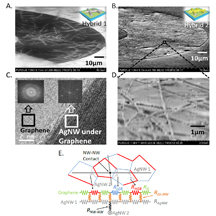 |
| Electron microscope images show a new material for transparent electrodes that might find uses in solar cells, flexible displays for computers and consumer electronics, and future "optoelectronic" circuits for sensors and information processing. The electrodes are made of silver nanowires covered with a material called graphene. At bottom is a model depicting the "co-percolating" network of graphene and silver nanowires. Purdue University image/Birck Nanotechnology Center |
Abstract:
Co-Percolating Graphene-Wrapped Silver Nanowire Network for High Performance, Highly Stable, Transparent Conducting Electrodes
Ruiyi Chen 1,4, Suprem R. Das 2,3, Changwook Jeong 1, Mohammad Ryyan Khan 1, David B. Janes 1,3,*, Muhammad A. Alam 1,*
1School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University,
2Department of Physics, Purdue University
3Birck Nanotechnology Center, Purdue University
4 Department of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027, China
Email: David B. Janes ( ), Muhammad A. Alam ( )
Transparent conducting electrodes (TCEs) require high transparency and low sheet resistance for applications in photovoltaics, photodetectors, flat panel displays, touch screen devices and imagers. Indium tin oxide (ITO), or other transparent conductive oxides, have typically been used, and provide a baseline sheet resistance (RS) vs. transparency (T) relationship. However, ITO is relatively expensive (due to limited abundance of Indium), brittle, unstable, and inflexible; moreover, ITO transparency drops rapidly for wavelengths above 1,000 nm. Motivated by a need for transparent conductors with comparable (or better) R Sat a given T, as well as flexible structures, several alternative material systems have been investigated. Single-layer graphene (SLG) or few-layer graphene provide sufficiently high transparency (≈97% per layer) to be a potential replacement for ITO. However, large-area synthesis approaches, including chemical vapor deposition (CVD), typically yield films with relatively high sheet resistance due to small grain sizes and high-resistance grain boundaries (HGBs). In this paper, we report a hybrid structure employing a CVD SLG film and a network of silver nanowires (AgNWs): RS as low as 22 Ω/□ (stabilized to 13 Ω/□ after 4 months) have been observed at high transparency (88% at λ = 550 nm) in hybrid structures employing relatively low-cost commercial graphene with a starting RSof 770 Ω/□. This sheet resistance is superior to typical reported values for ITO, comparable to the best reported TCEs employing graphene and/or random nanowire networks, and the film properties exhibit impressive stability under mechanical pressure, mechanical bending and over time. The design is inspired by the theory of a co-percolating network where conduction bottlenecks of a 2D film (e.g., SLG, MoS2) are circumvented by a 1D network (e.g., AgNWs, CNTs) and vice versa. The development of these high-performance hybrid structures provides a route towards robust, scalable and low-cost approaches for realizing high-performance TCE.
Innovation could bring flexible solar cells, transistors, displays
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on May 22nd, 2013Researchers have created a new type of transparent electrode that might find uses in solar cells, flexible displays for computers and consumer electronics and future "optoelectronic" circuits for sensors and information processing.
The electrode is made of silver nanowires covered with a material called graphene, an extremely thin layer of carbon. The hybrid material shows promise as a possible replacement for indium tin oxide, or ITO, used in transparent electrodes for touch-screen monitors, cell-phone displays and flat-screen televisions. Industry is seeking alternatives to ITO because of drawbacks: It is relatively expensive due to limited abundance of indium, and it is inflexible and degrades over time, becoming brittle and hindering performance.
"If you try to bend ITO it cracks and then stops functioning properly," said Purdue University doctoral student Suprem Das.
The hybrid material could represent a step toward innovations, including flexible solar cells and color monitors, flexible "heads-up" displays in car windshields and information displays on eyeglasses and visors.
"The key innovation is a material that is transparent, yet electrically conductive and flexible," said David Janes, a professor of electrical and computer engineering.
Research findings were detailed in a paper appearing online in April in the journal Advanced Functional Materials. The paper is available online at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.201300124/full. It was authored by Das; visiting student Ruiyi Chen; graduate students Changwook Jeong and Mohammad Ryyan Khan; Janes and Muhammad A. Alam, a Purdue professor of electrical and computer engineering.
The hybrid concept was proposed in earlier publications by Purdue researchers, including a 2011 paper in the journal Nano Letters. The concept represents a general approach that could apply to many other materials, said Alam, who co-authored the Nano Letters paper.
"This is a beautiful illustration of how theory enables a fundamental new way to engineer material at the nanoscale and tailor its properties," he said.
Such hybrid structures could enable researchers to overcome the "electron-transport bottleneck" of extremely thin films, referred to as two-dimensional materials.
Combining graphene and silver nanowires in a hybrid material overcomes drawbacks of each material individually: the graphene and nanowires conduct electricity with too much resistance to be practical for transparent electrodes. Sheets of graphene are made of individual segments called grains, and resistance increases at the boundaries between these grains. Silver nanowires, on the other hand, have high resistance because they are randomly oriented like a jumble of toothpicks facing in different directions. This random orientation makes for poor contact between nanowires, resulting in high resistance.
"So neither is good for conducting electricity, but when you combine them in a hybrid structure, they are," Janes said.
The graphene is draped over the silver nanowires.
"It's like putting a sheet of cellophane over a bowl of noodles," Janes said. "The graphene wraps around the silver nanowires and stretches around them."
Findings show the material has a low "sheet resistance," or the electrical resistance in very thin layers of material, which is measured in units called "squares." At 22 ohms per square, it is five times better than ITO, which has a sheet resistance of 100 ohms per square.
Moreover, the hybrid structure was found to have little resistance change when bent, whereas ITO shows dramatic increases in resistance when bent.
"The generality of the theoretical concept underlying this experimental demonstration - namely 'percolation-doping' -- suggests that it is likely to apply to a broad range of other 2-D nanocrystaline material, including graphene," Alam said.
A patent application has been filed by Purdue's Office of Technology Commercialization.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Emil Venere
765-494-4709
Sources:
David Janes
765-494-9263
Suprem Das
Muhammad A. Alam
765-494-5988
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Flexible Electronics
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Patents/IP/Tech Transfer/Licensing
![]() Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
Getting drugs across the blood-brain barrier using nanoparticles March 3rd, 2023
![]() Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
Metasurfaces control polarized light at will: New research unlocks the hidden potential of metasurfaces August 13th, 2021
![]() Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Announces Closing of Agreement with Takeda November 27th, 2020
Energy
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
The efficient perovskite cells with a structured anti-reflective layer – another step towards commercialization on a wider scale October 6th, 2023
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
![]() Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
Shedding light on unique conduction mechanisms in a new type of perovskite oxide November 17th, 2023
![]() Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
Inverted perovskite solar cell breaks 25% efficiency record: Researchers improve cell efficiency using a combination of molecules to address different November 17th, 2023
![]() Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
Charged “molecular beasts” the basis for new compounds: Researchers at Leipzig University use “aggressive” fragments of molecular ions for chemical synthesis November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








