Home > Press > A KAIST research team developed in vivo flexible large scale integrated circuits
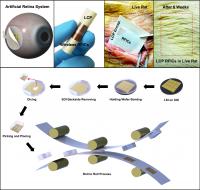 |
| This shows: Top: In vivo flexible large scale integrated circuits (LSI); Bottom: Schematic of roll-to-roll printing of flexible LSI on large area plastics.
Credit: KAIST |
Abstract:
A team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed in vivo silicon-based flexible large scale integrated circuits (LSI) for bio-medical wireless communication.
Fabrication process for flexible LSI for flexible display, wearable computer and artificial retina for in vivo biomedical application
A KAIST research team developed in vivo flexible large scale integrated circuits
Daejeon, Republic of Korea | Posted on May 6th, 2013Silicon-based semiconductors have played significant roles in signal processing, nerve stimulation, memory storage, and wireless communication in implantable electronics. However, the rigid and bulky LSI chips have limited uses in in vivo devices due to incongruent contact with the curvilinear surfaces of human organs. Especially, artificial retinas recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (refer to the press release of FDA's artificial retina approval) require extremely flexible and slim LSI to incorporate it within the cramped area of the human eye.
Although several research teams have fabricated flexible integrated circuits (ICs, tens of interconnected transistors) on plastics, their inaccurate nano-scale alignment on plastics has restricted the demonstration of flexible nano-transistors and their large scale interconnection for in vivo LSI applications such as main process unit (MPU), high density memory and wireless communication. Professor Lee's team previously demonstrated fully functional flexible memory using ultrathin silicon membranes (Nano Letters, Flexible Memristive Memory Array on Plastic Substrates), however, its integration level and transistor size (over micron scale) have limited functional applications for flexible consumer electronics.
Professor Keon Jae Lee's team fabricated radio frequency integrated circuits (RFICs) interconnected with thousand nano-transistors on silicon wafer by state-of-the-art CMOS process, and then they removed the entire bottom substrate except top 100 nm active circuit layer by wet chemical etching. The flexible RF switches for wireless communication were monolithically encapsulated with biocompatible liquid crystal polymers (LCPs) for in vivo bio-medical applications. Finally, they implanted the LCP encapsulated RFICs into live rats to demonstrate the stable operation of flexible devices under in vivo circumstances.
Professor Lee said, "This work could provide an approach to flexible LSI for an ideal artificial retina system and other bio-medical devices. Moreover, the result represents an exciting technology with the strong potential to realize fully flexible consumer electronics such as application processor (AP) for mobile operating system, high-capacity memory, and wireless communication in the near future."
This result was published in the May online issue of the American Chemical Society's journal, ACS Nano (In vivo Flexible RFICs Monolithically Encapsulated with LCP). They are currently engaged in commercializing efforts of roll-to-roll printing of flexible LSI on large area plastic substrates.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lan Yoon
82-423-502-295
Copyright © KAIST
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








