Home > Press > Boston College researchers' unique nanostructure produces novel 'plasmonic halos': Nanoscopic microcavities offer newfound control in light filtering
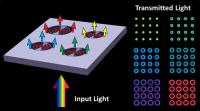 |
| Boston College researchers have constructed a unique nanostructure that exploits microcavity features to filter visible light into "plasmonic halos" of selected color output. The device could have applications in areas such as biomedical plasmonics or discrete optical filtering.
Credit: Nano Letters |
Abstract:
Using the geometric and material properties of a unique nanostructure, Boston College researchers have uncovered a novel photonic effect where surface plasmons interact with light to form "plasmonic halos" of selectable output color. The findings appear in the journal Nano Letters.
Boston College researchers' unique nanostructure produces novel 'plasmonic halos': Nanoscopic microcavities offer newfound control in light filtering
Chestnut Hill, MA | Posted on February 7th, 2013The novel nanostructure proved capable of manipulating electron waves known as surface plasmon polaritons, or SPPs, which were discovered in the 1950s but of late have garnered the attention of scientists for their potential applications in fields that include waveguiding, lasing, color filtering and printing.
The team put a layer of a polymer film on a glass substrate and then dotted the surface with holes precisely defined by a process of electron beam lithography, using the BC Integrated Sciences Nanofabrication Clean Room facility. The team next applied a layer of silver, thick enough to be nontransparent to visible light. In addition to covering the thin film on top, the silver coated the contours of the holes in the film, as well as the exposed circles of the glass substrate below. The effect produced an array of silver microcavities.
When the researchers directed light from below and through the glass substrate, light "leaking" through nanoscale gaps on the perimeters of the microcavities created SPP waves on their top surfaces. At particular wavelengths of the incident light, these waves formed modes or resonances analogous to acoustic waves on a drumhead, which in turn effectively filtered the light transmitted to the far side, accounting for the "halo" appearance, said Boston College Ferris Professor of Physics Michael Naughton, who co-authored the report with Senior Research Associate Michael J. Burns and doctoral student and lead author Fan Ye. The team's research was funded by the W. M. Keck Foundation.
Central to this control effect are "step gaps" formed along the perimeter of each circle, which give the nanostructure the ability to modulate which waves of light pass through. It is within this geometry that the interaction of light upon the silver surface coating resulted in the excitation of plasmon waves, said Naughton. Examination of the SPPs by Mr. Ye using a near-field scanning optical microscope offered unique insights into the physics at work within the structure, Naughton said.
By adjusting the type of metal used to coat the structure or varying the circumferences of the microcavities, Naughton said the step-gap structure is capable of manipulating the optical properties of the device in the visible light range, giving the researchers newfound control in light filtering.
This kind of control, the team reports, could have applications in areas such as biomedical plasmonics or discrete optical filtering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ed Hayward
617-552-4826
Copyright © Boston College
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Thin films
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
![]() Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Observation of left and right at nanoscale with optical force October 6th, 2023
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








