Home > Press > Tiny capsule effectively kills cancer cells: Scientists create nanoscale vehicle to battle cancer without harming healthy cells
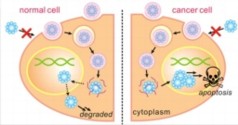 |
| A diagram of the synthesis of degradable nanocapsules into cell nuclei to induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in cancer cells. The nanocapsules degrade harmlessly in normal cells.
(Courtesy of UCLA Engineering) |
Abstract:
A tiny capsule invented at a UCLA lab could go a long way toward improving cancer treatment.
Devising a method for more precise and less invasive treatment of cancer tumors, a team led by researchers from the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science has developed a degradable nanoscale shell to carry proteins to cancer cells and stunt the growth of tumors without damaging healthy cells.
Tiny capsule effectively kills cancer cells: Scientists create nanoscale vehicle to battle cancer without harming healthy cells
Los Angeles, CA | Posted on February 6th, 2013In a new study, published online Feb. 1 in the peer-reviewed journal Nano Today, a group led by Yi Tang, a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and a member of the California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA, reports developing tiny shells composed of a water-soluble polymer that safely deliver a protein complex to the nucleus of cancer cells to induce their death. The shells, which at about 100 nanometers are roughly half the size of the smallest bacterium, degrade harmlessly in non-cancerous cells.
The process does not present the risk of genetic mutation posed by gene therapies for cancer, or the risk to healthy cells caused by chemotherapy, which does not effectively discriminate between healthy and cancerous cells, Tang said.
"This approach is potentially a new way to treat cancer," said Tang. "It is a difficult problem to deliver the protein if we don't use this vehicle. This is a unique way to treat cancer cells and leave healthy cells untouched."
The cell-destroying material, apoptin, is a protein complex derived from an anemia virus in birds. This protein cargo accumulates in the nucleus of cancer cells and signals to the cell to undergo programmed self-destruction.
The polymer shells are developed under mild physiological conditions so as not to alter the chemical structure of the proteins or cause them to clump, preserving their effectiveness on the cancer cells.
Tests done on human breast cancer cell lines in laboratory mice showed significant reduction in tumor growth.
"Delivering a large protein complex such as apoptin to the innermost compartment of tumor cells was a challenge, but the reversible polymer encapsulation strategy was very effective in protecting and escorting the cargo in its functional form," said Muxun Zhao, lead author of the research and a graduate student in chemical and biomolecular engineering at UCLA.
Tang's group continues to research ways of more precisely targeting tumors, prolonging the circulation time of the capsules and delivering other highly sought-after proteins to cancer cells.
The research team also included former UCLA Engineering student Zhen Gu, now an assistant professor in the joint biomedical engineering department at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and North Carolina State University, and University of Southern California researchers including graduate student Biliang Hu, postdoctoral scholar Kye-Il Joo and associate professor Pin Wang.
The Nano Today paper also will be published in a future print edition of the journal.
The research was funded by the David and Lucille Packard Foundation and a breast cancer research grant from the Congressionally Directed Medical Research Program.
####
About University of California - Los Angeles
The UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science, established in 1945, offers 28 academic and professional degree programs and has an enrollment of more than 5,000 students. The school's distinguished faculty are leading research to address many of the critical challenges of the 21st century, including renewable energy, clean water, health care, wireless sensing and networking, and cybersecurity. Ranked among the top 10 engineering schools at public universities nationwide, the school is home to nine multimillion-dollar interdisciplinary research centers in wireless sensor systems, wireless health, nanoelectronics, nanomedicine, renewable energy, customized computing, the smart grid, and the Internet, all funded by federal and private agencies and individual donors. (www.engineer.ucla.edu | www.twitter.com/uclaengineering)
For more UCLA news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Bill Kisliuk
310-206-0540
Copyright © University of California - Los Angeles
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








