Home > Press > Essential armchair reading for nanotube researchers: Rice, NIST kick off collaboration with comprehensive look at the fundamentals of most desirable nanotubes
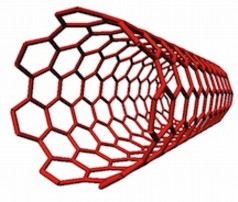 |
| Armchair carbon nanotubes, so named for the arrangement of atoms that make their ends look like armchairs, are the most desirable among nanotube researchers for their superior electrical properties. They are the subject of a new paper by Rice University and the National Institute of Standards and Technology. (Credit: Erik Hároz/Rice University) |
Abstract:
The first fruits of a cooperative venture between scientists at Rice University and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have appeared in a paper that brings together a wealth of information for those who wish to use the unique properties of metallic carbon nanotubes.
Essential armchair reading for nanotube researchers: Rice, NIST kick off collaboration with comprehensive look at the fundamentals of most desirable nanotubes
Houston, TX | Posted on February 5th, 2013The feature article published recently in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Nanoscale gathers research about the separation and fundamental characteristics of armchair carbon nanotubes, which have been of particular interest to researchers trying to tune their electronic and optical properties.
This paper, said Rice physicist Junichiro Kono, provides scientists a valuable resource for detailed information about metallic carbon nanotubes, especially armchair nanotubes. "Basically, we summarized all our recent findings as well as all information we could find in the literature about metallic nanotubes, along with detailed accounts of preparation methods for metal-enriched nanotube samples, to show the community just how much we now understand about these one-dimensional metals," he said.
As part of the lengthy work, the team compiled and published tables of essential statistics, including optical properties, for a variety of metallic nanotubes. "We provide fundamental theoretical backgrounds and then show very detailed experimental results on unique properties of metallic nanotubes," Kono said. "This paper summarizes what kind of aspects are understood, and what is not, about fundamental optical processes in nanotubes and will make it easier for researchers to identify their spectroscopic features and transition energies."
Nanotubes come in many flavors, depending on their chirality. Chirality is a characteristic akin to the angles at which a flat sheet of paper might align when wrapped into a tube. Cut the tube in half and the atoms at the open edge would line up in the shape of an armchair, a zigzag or some variant. Even though their raw material is identical - chicken-wire-like hexagons of carbon - the chirality makes all the difference in how nanotubes transmit electricity.
Armchairs are the most coveted because they have no band gap; electrons flow through without resistance. Cables made with armchair nanotubes have the potential to move electricity over great distances with virtually no loss. That makes them the gold standard as the basic element of armchair quantum wire. The ongoing development of this very strong, lightweight, high-capacity cable could improve further the record properties of multifunctional carbon nanotube fibers that are being developed by the group of Rice Professor Matteo Pasquali.
The new work led by Kono and Robert Hauge, a distinguished faculty fellow in chemistry at Rice, along with scientists at NIST and Los Alamos National Laboratory, looks beyond the armchair's established electrical properties to further detail their potential for electronic, sensing, optical and photonic devices.
"Of course, to get there, we need really good samples," Kono said. "Many applications will rely on our ability to separate carbon nanotubes and then assemble macroscopically ordered structures consisting of single-chirality nanotubes. Nobody can do that at this point."
When a batch of nanotubes comes out of a furnace, it's a jumble of types. That makes detailed analysis of their characteristics -- let alone their practical use -- a challenge.
But techniques developed in recent years at Rice and by NIST scientist Ming Zheng to purify metallic nanotubes are beginning to change that. Rice graduate student Erik Hároz said recent experiments established "unambiguous evidence" that a process he and Kono are using called density gradient ultracentrifugation can enrich ensemble samples of armchairs. Taking things further, Zheng's method of DNA-based ion-exchange chromatography provides very small samples of ultrapure armchair nanotubes of a single chirality.
Rice and NIST are now looking at ways to combine the methods to get larger batches of a specific armchair chirality, Kono said.
If anyone can accomplish such a breakthrough, these labs can, he said. "Our team has the best possible armchair samples available due to these two methods, and we have recently made significant progress in increasing our understanding of the properties of armchair nanotubes, as described in this Nanoscale article."
Co-authors of the paper with Hároz, Hauge, Zheng and Kono are Juan Duque, who earned his doctorate at Rice and is now a research scientist at Los Alamos; Xiaomin Tu, a former postdoctoral researcher at NIST, now an intellectual property subject matter expert at Chevron; Angela Hight Walker, project leader in the Semiconductor and Dimensional Metrology Division at NIST; and Stephen Doorn, science partner leader in the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies at Los Alamos. Kono is a professor of electrical and computer engineering and of physics and astronomy at Rice. Pasquali is a professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and of chemistry.
The National Science Foundation, the Department of Energy, the Air Force Research Laboratories, Los Alamos National Laboratory, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, NASA and the World Class University Program at Sungkyunkwan University supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Richard E. Smalley Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology:
Richard E. Smalley Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology:
![]() Nano parfait a treat for scientists:
Nano parfait a treat for scientists:
![]() DNA-assisted dispersion and separation of carbon nanotubes:
DNA-assisted dispersion and separation of carbon nanotubes:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings
![]() Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
Tests find no free-standing nanotubes released from tire tread wear September 8th, 2023
![]() Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Detection of bacteria and viruses with fluorescent nanotubes July 21st, 2023
Sensors
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








