Home > Press > May the force be with the atomic probe: New models suggest devising means of probing a surface at a sub-micrometric level as this will help us understand how electrons’ diffusion affects long-range attractive forces
 |
Abstract:
Theoretical physicist Elad Eizner from Ben Gurion University, Israel, and colleagues created models to study the attractive forces affecting atoms located at a wide range of distances from a surface, in the hundreds of nanometers range. Their results, about to be published in EPJ D, show that these forces depend on electron diffusion, regardless of whether the surface is conducting or not. Ultimately, these findings could contribute to designing minimally invasive surface probes.
May the force be with the atomic probe: New models suggest devising means of probing a surface at a sub-micrometric level as this will help us understand how electrons’ diffusion affects long-range attractive forces
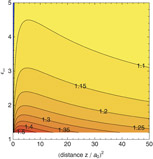
New York, NY and Heidelberg, Germany | Posted on December 21st, 2012Bombarding a surface with atoms helps us understand the distribution of its electrons and the structural arrangement of the surface atoms. The authors focused on understanding how a long-range force— referred to as the van der Waals-Casimir-Polder (vdW-CP) force — present between an atom and a surface allow us to distinguish surface characteristics on the basis of their conductivity.
A key factor in understanding the behaviour of the force, they realised, is the size of the electron cloud surrounding an impurity charge in the system. The latter depends both on the electrons' conductivity and their capability to diffuse in and along the surface.
They devised one model for the diffusion of the electronic charge in the bulk of the material and another one in the near-surface region. They tested their models on both conducting and non-conducting surfaces. They were thus able to explain why the atom-surface force shows a continuous transition in terms of conductivity between both types of surfaces.
For distances comparable to the size of the electron cloud spread, the strength of the vdW-CP attraction force, they found, can help distinguish between bulk and surface electrons diffusion. It could therefore be used as a probe. Potential applications exist, for example, in quantum computer hardware architectures focusing on the interface between different carriers of quantum bits of information.
Reference:
E.Eizner, B. Horovitz, and C. Henkel (2012), Van der Waals-Casimir-Polder interaction of an atom with a composite surface, European Physical Journal D, DOI: 10.1140/epjd/e2012-30294-x
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ann Koebler
49-622-148-78414
Copyright © Springer
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Quantum Computing
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








