Home > Press > The best of both catalytic worlds
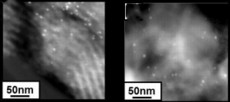 |
| Heterogenized homogeneous nanocatalysts are sustainable as shown by these TEM images in which there is almost no difference in the cluster size of dendrimer-encapsulated gold nanoclusters (white spots) before (left) and after cyclopropanation reactions. |
Abstract:
Catalysts are substances that speed up the rates of chemical reactions without themselves being chemically changed. Industrial catalysts come in two main types - heterogeneous, in which the catalyst is in a different phase from the reactants; and homogeneous, in which catalyst and the reactants are in the same phase. Heterogeneous catalysts are valued for their sustainability because they can be recycled. Homogeneous catalysts are valued for their product selectivity as their properties can be easily tuned through relatively simple chemistry.
The best of both catalytic worlds
Berkeley, CA | Posted on October 10th, 2012Researchers with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have combined the best properties of both types of industrial catalysts by encapsulating nanoclusters of a metallic heterogeneous catalyst within the branched arms of the molecules known as dendrimers.
The results are heterogenized homogeneous nanocatalysts that are sustainable and feature high reactivity and selectivity. Furthermore, these heterogenized homogeneous nanocrystals hold promise for bridging the gap between industrial catalysts, which carry out simple reactions, and a third type of catalyst, the proteins known as enzymes, that nature uses to carry out the complex reactions of biochemistry.
"Using cyclopropanation reactions catalyzed by dendrimer-encapsulated gold and other metal nanoclusters, including platinum, palladium and rhodium, we have demonstrated that changing the dendrimer properties allows catalytic reactivity in a heterogeneous catalyst to be tuned in a similar fashion to ligand modification in a homogeneous catalyst," says world renowned catalysis chemist Gabor Somorjai, one of the leaders of this research. "Furthermore, we have shown that these heterogeneous catalysts employed in a fixed-bed flow reactor allow fine control over the residence time of the reactants and thus enable control over product distribution in a way that is not easily available for homogeneous catalysts."
Somorjai is a senior scientist with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division, where he directs the Surface Science and Catalysis Program, and a professor of chemistry with the Chemistry Department at the University of California Berkeley. He is the corresponding author along with chemist Dean Toste, who also holds joint appointments with Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley, of a paper describing this research in the journal Nature Chemistry. The paper is titled "Control of selectivity in heterogeneous catalysis by tuning nanoparticle properties and reactor residence time." Other authors were Elad Gross and Jack Hung-Chang Liu.
Catalysts are used to initiate virtually every industrial manufacturing process that involves chemistry. Metal catalysts have been the traditional workhorses, but in recent years nano-sized catalysts have surged in importance.
"From our work, it has become increasingly clear that at the molecular level, all catalysts - heterogeneous, homogeneous and enzymes - function the same," Somorjai says. "We have now proven that working with metal nanoclusters, the same chemistry can be done with heterogeneous or homogeneous catalysts."
Adds corresponding author Dean Toste, "It's an exciting prospect that there may be universal design principles that can be applied to constructing 100-percent selective catalysts, whether they are homogeneous or heterogeneous. Ultimately, if these principles can be uncovered, it should be possible to design complex networks of selective catalysts that generate products with high efficiency."
The key to the success of this latest research was the encapsulation of metal nanoparticles inside dendrimers. The term "dendrimer" comes from the Greek word for "tree," an apt description for branching polymer molecules that resemble a worm's eye view of a tree's root system. Somorjai, Toste and their co-authors used gold nanoclusters and polyamidoamine (PAMAM), a common class of dendrimers suitable for numerous applications in materials and biotechnology. They successfully tested their dendrimer-encapsulated catalyst on cyclopropane, a biomolecule widely used in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries, and typically formed through homogeneous catalysis.
"By designing the molecular architecture of our catalyst to feature a highly crowded matrix, we greatly enhanced the product selectivity of our reaction, similar to the use of bulky ligands in a homogeneous catalyst," says Elad Gross, the lead author of the Nature Chemistry paper and a member of Somorjai's research group. "Product selectivity was further enhanced by employing the catalyst in a flow reactor and changing the flow rate of the reactants. This gave us a high degree of control over our secondary reactions, again similar to the role that ligand electronic properties play in tuning the chemical selectivity of homogeneous catalysts."
Given that flow systems are widely used in industrial chemistry, the concept of replacing homogeneous catalysts with dendrimer-encapsulated heterogeneous catalysts whose product selectivity can be controlled should be a popular alternative. For example, the catalysis of cyclopropane could be tuned to favor the formation of cyclopropanes that are critical components of cancer and cholesterol medicines. The recyclability of these dendrimer-encapsulated heterogeneous catalysts is another major advantage.
"Highly selective catalysts, especially those that can be recycled readily, are vital for the development of sustainable chemical processes," Gross says. "In the future, with our technique it should be possible to combine heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts to get specific products with very high selectivity."
This research was supported by the DOE Office of Science.
####
About Berkeley Lab
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world’s most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab’s scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science. For more, visit www.lbl.gov.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit the Office of Science website at science.energy.gov/.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
510-486-5375
Copyright © Berkeley Lab
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() For more about the research of Gabor Somorjai go here:
For more about the research of Gabor Somorjai go here:
![]() For more about the research of Dean Toste go here:
For more about the research of Dean Toste go here:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








