Home > Press > Oh, my stars and hexagons! DNA code shapes gold nanoparticles
 |
| Graphic by
Li Huey Tan, Zidong Wang and Yi Lu
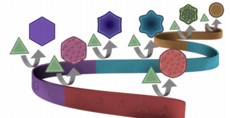
University of Illinois chemists found that DNA can shape gold nanoparticle growth similarly to the way it shapes protein synthesis, with different letters of the genetic code producing gold circles, stars and hexagons. |
Abstract:
DNA holds the genetic code for all sorts of biological molecules and traits. But University of Illinois researchers have found that DNA's code can similarly shape metallic structures.
Oh, my stars and hexagons! DNA code shapes gold nanoparticles
Champaign, IL | Posted on August 8th, 2012The team found that DNA segments can direct the shape of gold
nanoparticles - tiny gold crystals that have many applications in medicine, electronics and catalysis. Led by Yi Lu, the Schenck Professor of Chemistry at the U. of I., the team published its surprising findings in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
"DNA-encoded nanoparticle synthesis can provide us a facile but novel way to produce nanoparticles with predictable shape and properties," Lu said. "Such a discovery has potential impacts in bio-nanotechnology and applications in our everyday lives such as catalysis, sensing, imaging and medicine."
Gold nanoparticles have wide applications in both biology and materials science thanks to their unique physicochemical properties. Properties of a gold nanoparticle are largely determined by its shape and size, so it is critical to be able to tailor the properties of a nanoparticle for a specific application.
"We wondered whether different combinations of DNA sequences could constitute ‘genetic codes' to direct the nanomaterial synthesis in a way similar to their direction of protein synthesis," said Zidong Wang, a recent graduate of Lu's group and the first author of the paper.
Gold nanoparticles are made by sewing tiny gold seeds in a solution of gold salt. Particles grow as gold in the salt solution deposits onto the seeds. Lu's group incubated the gold seeds with short segments of DNA before adding the salt solution, causing the particles to grow into various shapes determined by the genetic code of the DNA.
The DNA alphabet comprises four letters: A, T, G and C. The term genetic code refers to the sequence of these letters, called bases. The four bases and their combinations can bind differently with facets of gold nanoseeds and direct the nanoseeds' growth pathways, resulting in different shapes.
In their experiments, the researchers found that strands of repeating A's produced rough, round gold particles; T's, stars; C's, round, flat discs; G's, hexagons. Then the group tested DNA strands that were a combination of two bases, for example, 10 T's and 20 A's. They found that many of the bases compete with each other resulting in intermediate shapes, although A dominates over T.
Next, the researchers plan to investigate exactly how DNA codes direct nanoparticle growth. They also plan to apply their method to synthesize other types of nanomaterials with novel applications.
The National Science Foundation supported this work.
Lu also is affiliated with the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology and with the Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory, both of which are at the U. of I.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liz Ahlberg
Physical Sciences Editor
217-244-1073
Copyright © University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








