Home > Press > Switchable nano magnets: Research group at Kiel University switches magnetism of individual molecules
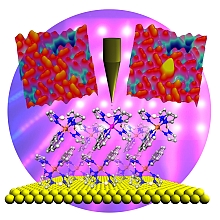 |
| Computer graphic of the spin-crossover molecule that was used for the experiments on gold surface and the STM images of its different magnetic states Picure & copyright: Holger Naggert & Thiruvancheril Gopakumar |
Abstract:
Using individual molecules instead of electronic or magnetic memory cells would revolutionise data storage technology, as molecular memories could be thousand-fold smaller. Scientists of Kiel University took a big step towards developing such molecular data storage. They succeeded in selectively switching on and off the magnetism of individual molecules, so-called spin-crossover complexes, by electrons. The interdisciplinary study is part of the Collaborative Research Centre 677 "Functions by Switching", which is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG). The results prove that it is technically possible to store information using molecules. The study will be published on June 25th in the German science magazine "Angewandte Chemie" (Applied Chemistry).
Switchable nano magnets: Research group at Kiel University switches magnetism of individual molecules
Kiel, Germany | Posted on June 14th, 2012"In principle information may be stored in a single molecule. However, techniques that would make such an approach feasible are becoming available just now", explains project leader Professor Richard Berndt of the Institute of Experimental and Applied Physics at Kiel University. Since the 1980s scientists are able to image individual molecules on surfaces with scanning tunnelling microscopes, he continues. Current research aims at controlling the characteristics of single molecules in order to facilitate future technical applications. The Collaborative Research Centre 677 "Functions by Switching" at Kiel University is a large-scale project engaged in such investigations, which aim at constructing molecular machines.
The current study is focused on the magnetism of molecules. Using a scanning tunnelling microscope Dr. Thiruvancheril Gopakumar, who carried out the study, was able to switch individual molecules between two magnetic states. Despite their dense packing in a molecular layer he was able to target individual molecules for switching. "Many research groups are striving to control the magnetic characteristics of molecules. Gopakumar's studies have taken us one step ahead", says Berndt.
The molecules (spin-crossover complexes) were synthesised at the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry at Kiel University. "Even though it took us a long time to find adequate molecules, we are very pleased with the outcome", states Professor Felix Tuczek, head of the research group "Inorganic Molecular Chemistry". The next step will be to adapt the molecules in a way that would allow scientists to switch them with light instead of electrons and at higher temperatures.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Prof. Dr. Richard Berndt
Institut für Experimentelle und Angewandte Physik
phone: +49 (431) 880-3946
Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel
Press and Communication Services
Dr. Boris Pawlowski
Text: Stefanie Maack
Address: D-24098 Kiel
phone: +49 (0431) 880-2104
fax: +49 (0431) 880-1355
Copyright © Kiel University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Further information about CRC 677:
Further information about CRC 677:
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Memory Technology
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance June 9th, 2023
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








