Home > Press > UMD graphene photodetector offers better weapons detectors & scanners, telescopes to study dark energy
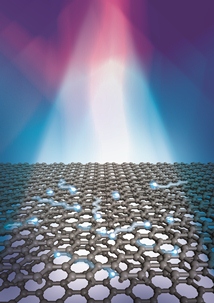 |
| Electrons in bilayer graphene are heated by a beam of light. Illustration by Loretta Kuo and Michelle Groce, University of Maryland. |
Abstract:
Innovation promises better biochemical weapons detection and body scanners, and new instruments for studying dark energy & the structure of the universe.
UMD graphene photodetector offers better weapons detectors & scanners, telescopes to study dark energy
College Park, MD | Posted on June 3rd, 2012Researchers at the Center for Nanophysics and Advanced Materials of the University of Maryland have developed a new type of hot electron bolometer a sensitive detector of infrared light, that can be used in a huge range of applications from detection of chemical and biochemical weapons from a distance and use in security imaging technologies such as airport body scanners, to chemical analysis in the laboratory and studying the structure of the universe through new telescopes.
The UMD researchers, led by Research Associate Jun Yan and Professors Michael Fuhrer and Dennis Drew, developed the bolometer using bilayer graphene--two atomic-thickness sheets of carbon. Due to graphene's unique properties, the bolometer is expected to be sensitive to a very broad range of light energies, ranging from terahertz frequencies or submillimeter waves through the infrared to visible light.
The graphene hot electron bolometer is particularly promising as a fast, sensitive, and low-noise detector of submillimeter waves, which are particularly difficult to detect. Because these photons are emitted by relatively cool interstellar molecules, submillimeter astronomy studies the early stages of formation of stars and galaxies by observing these interstellar clouds of molecules. Sensitive detectors of submillimeter waves are being sought for new observatories that will determine the redshifts and masses of very distant young galaxies and enable studies of dark energy and the development of structure in the universe.
The Maryland team's findings are published in the June 3 issue of Nature Nanotechnology.
Most photon detectors are based on semiconductors. Semiconductors are materials which have a range of energies that their electrons are forbidden to occupy, called a "band gap". The electrons in a semiconductor can absorb photons of light having energies greater than the band gap energy, and this property forms the basis of devices such as photovoltaic cells.
Graphene, a single atom-thick plane of graphite, is unique in that is has a bandgap of exactly zero energy; graphene can therefore absorb photons of any energy. This property makes graphene particularly attractive for absorbing very low energy photons (terahertz and infrared) which pass through most semiconductors. Graphene has another attractive property as a photon absorber: the electrons which absorb the energy are able to retain it efficiently, rather than losing energy to vibrations of the atoms of the material. This same property also leads to extremely low electrical resistance in graphene.
University of Maryland researchers exploited these two properties to devise the hot electron bolometer. It works by measuring the change in the resistance that results from the heating of the electrons as they absorb light.
Normally, graphene's resistance is almost independent of temperature, unsuitable for a bolometer. So the Maryland researchers used a special trick: when bilayer graphene is exposed to an electric field it has a small band gap, large enough that its resistance becomes strongly temperature dependent, but small enough to maintain its ability to absorb low energy infrared photons.
The researchers found that their bilayer graphene hot electron bolometer operating at a temperature of 5 Kelvin had comparable sensitivity to existing bolometers operating at similar temperatures, but was more than a thousand times faster. They extrapolated the performance of the graphene bolometer to lower temperature and found that it may beat all existing technologies.
Some challenges remain. The bilayer graphene bolometer has a higher electrical resistance than similar devices using other materials which may make it difficult to use at high frequencies. Additionally, bilayer graphene absorbs only a few percent of incident light. But the Maryland researchers are working on ways to get around these difficulties with new device designs, and are confident that a graphene has a bright future as a photo-detecting material.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Science Contact: Dr. Michael S. Fuhrer
Phone: (301) 405-6143
Copyright © University of Maryland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Homeland Security
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
Sensors developed at URI can identify threats at the molecular level: More sensitive than a dog's nose and the sensors don't get tired May 21st, 2021
![]() Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Highly sensitive dopamine detector uses 2D materials August 7th, 2020
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Aerospace/Space
![]() Under pressure - space exploration in our time: Advancing space exploration through diverse collaborations and ethical policies February 16th, 2024
Under pressure - space exploration in our time: Advancing space exploration through diverse collaborations and ethical policies February 16th, 2024
![]() Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
Bridging light and electrons January 12th, 2024
![]() Manufacturing advances bring material back in vogue January 20th, 2023
Manufacturing advances bring material back in vogue January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








