Home > Press > Atomic-scale Visualization of Electron Pairing in Iron Superconductors: Findings support magnetic pairing theory that could lead to new improved superconductors
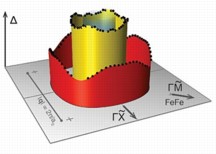 |
| Data supports role of magnetism in iron-based superconductors: The height of each dot in this image represents the superconducting energy gap — a measure of the strength of electron pairing — for electrons moving at a particular momentum (speed in a given direction) on each electronic band (red and yellow rings) of a particular iron superconductor. The data show that the magnitude of the gap (height of the dots) varies by its momentum (position along the base plane) and the band it is on — which is exactly what was predicted by theories in which magnetism plays a primary role in the emergence of superconductivity. The results therefore strengthen confidence that those theories may help scientists discover or design new superconductors. |
Abstract:
By measuring how strongly electrons are bound together to form Cooper pairs in an iron-based superconductor, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory, Cornell University, St. Andrews University, and collaborators provide direct evidence supporting theories in which magnetism holds the key to this material's ability to carry current with no resistance. Because the measurements take into account the electronic bands and directions in which the electrons are traveling, which was central to testing the theoretical predictions, this research strengthens confidence that this type of theory may one day be used to identify or design new materials with improved properties - namely, superconductors operating at temperatures far higher than today's.
Atomic-scale Visualization of Electron Pairing in Iron Superconductors: Findings support magnetic pairing theory that could lead to new improved superconductors
Upton, NY | Posted on May 3rd, 2012The findings are published in the May 4, 2012 issue of Science.
"In the best possible world you would be able to take this theory and plug in different chemical elements until you find a combination that should work as a superconductor at higher temperatures," said team leader Séamus Davis, Director of the Center for Emergent Superconductivity (http://www.bnl.gov/energy/ces/) at Brookhaven and the J.G. White Distinguished Professor of Physical Sciences at Cornell University. Such materials could be used for real world, energy-saving technologies, such as zero-loss power transmission lines, without the need for expensive coolants.
Scientists have been trying to understand the mechanism underlying so-called "high-temperature" superconductivity ever since discovering materials that could carry current with no resistance at temperatures somewhat above the operating realm of conventional superconductors, which must be chilled to near absolute zero (0 kelvin, or -273° Celsius). Though still mighty chilly, these high-Tc materials' operating temperatures - some as high as 145K (-130°C) - offer hope that such materials could one day be designed to operate at room temperature.
One key to superconductivity is the formation of electron pairs. Scientists hypothesized that if these negatively charged particles have their magnetic moments pointing in opposite directions, they could overcome their mutual repulsion to join forces in so-called Cooper pairs - thus carrying current with no loss.
"Many people suspected you could take materials that naturally have alternating magnetic moments on adjacent electrons - antiferromagnetic materials - and convert them into superconductors," Davis said. But to prove this conjecture hasn't been possible with copper-based, or cuprate, superconductors - the first high-Tc superconductors discovered starting some 25 years ago. "You can make a robust antiferromagnetic cuprate insulator, but in that state it's hard to get the magnetic electrons to pair and then move around and make a superconductor," Davis said.
Then, in 2008, when iron-based superconductors were discovered, the idea that magnetism plays a role in high-Tc superconductivity was revived. But determining that role was a very complex problem.
"In each iron atom there are five magnetic electrons, not just one," Davis said. "And each, as it moves around the crystal, does so in a separate electronic band. In order to find out if the magnetic interactions between electrons are generating the superconductivity, you have to measure what's called the anisotropic energy gap - how strongly bound together the electrons are in a pair - depending on the electrons' directions on the different electronic bands."
Theorists Dung-Hai Lee of the University of California at Berkeley, Peter Hirschfeld of the University of Florida, and Andrey Chubukov of the University of Wisconsin among others had developed different versions of a theory that predicts what those measurements should be if magnetism were the mechanism for superconductivity.
"It was our job to test those predictions," Davis said. But at first, the techniques didn't exist to make the measurements. "We had to invent them," Davis said.
Two scientists working with Davis, Milan P. Allan of Brookhaven, Cornell, and the University of Saint Andrews (where Davis also teaches) and Andreas W. Rost of Cornell and St. Andrews - the lead authors on the paper - figured out how to do the experiments and identified an iron-based material (lithium iron arsenide) in which to test the predictions.
Their method, multi-band Bogoliubov quasiparticle scattering interference, found the "signature" predicted by the theorists:
"The strength of the 'glue' holding the pairs together is different on the different bands, and on each band it depends on the direction that the electrons are traveling - with the pairing usually being stronger in a given direction than at 45° to that direction," Davis said.
"This is the first experimental evidence direct from the electronic structure in support of the theories that the mechanism for superconductivity in iron-based superconductors is due primarily to magnetic interactions," he said.
The next step is to use the same technique to determine whether the theory holds true for other iron superconductors. "We and others are working on that now," Davis said.
If those experiments show that the theory is indeed correct, the model could then be used to predict the properties of other elements and combinations - and ideally point the way toward engineering new materials and higher-temperature superconductors.
This research was supported as part of the Center for Emergent Superconductivity, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science; the U.K. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council; the U.S. National Science Foundation; the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science; the Academia Sinica Research Program on Nanoscience & Nanotechnology; and a Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov/.
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation of State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit, applied science and technology organization.
Visit Brookhaven Lab's electronic newsroom for links, news archives, graphics, and more at www.bnl.gov/newsroom , or follow Brookhaven Lab on Twitter, twitter.com/BrookhavenLab .
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karen McNulty Walsh
(631) 344-8350
or Peter Genzer
(631) 344-3174
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Physics
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Superconductivity
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Laboratories
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








